Inflammation and nutritional status indicators as prognostic indicators for patients with locally advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors treated with neoadjuvant imatinib
- PMID: 36690935
- PMCID: PMC9869595
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-023-02658-x
Inflammation and nutritional status indicators as prognostic indicators for patients with locally advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors treated with neoadjuvant imatinib
Abstract
Background: Previous studies have confirmed that preoperative nutritional-inflammatory indicators can predict prognosis in various malignancies. However, to the best of our knowledge, no study has investigated the assessment of systemic inflammatory immunity index (SII) combined with prognostic nutritional index (PNI) scores to predict prognosis after neoadjuvant treatment with imatinib in locally advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumours (LA-GIST). The aim of this study was to evaluate the predictive value of pretreatment SII-PNI scores in predicting recurrence after neoadjuvant therapy with imatinib in patients with LA-GIST.
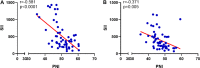
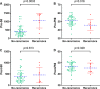
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 57 patients with LA-GIST who received imatinib neoadjuvant from January 2013 to March 2019. Patients were divided into recurrence and non-recurrence groups according to their follow-up status, and SII and PNI cut-offs were calculated by receiver operating characteristic. The SII-PNI score ranged from 0 to 2 and were categorized into the following: score of 2, high SII (≥ 544.6) and low PNI (≤ 47.2); score of 1, either high SII (≥ 544.6) or low PNI (≤ 47.2); score of 0, no high SII (≥ 544.6) nor low PNI (≤ 47.2).
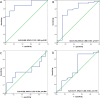
Results: All patients received imatinib neoadjuvant therapy for a median treatment period of 8.5 months (ranging from 3.2 to 12.6 months), with 8 patients (14.04%) and 49 patients (85.96%) developing recurrence and non-recurrence, respectively. Patients with a high SII-PNI score had a significantly worse recurrence-free survival time than those with a low SII-PNI score (P = 0.022, 0.046), and had a poorer pathological response (P = 0.014). Multivariate analysis demonstrated that the SII-PNI score was an independent prognostic factor for prediction of recurrence-free survival (P = 0.002).
Conclusion: The pre-treatment SII-PNI score can be used to predict the efficacy after neoadjuvant treatment with imatinib in patients with LA-GIST, which may be a promising predictor of recurrence-free survival time for patients.
Keywords: Gastrointestinal stromal tumors; Inflammation; Neoadjuvant therapy; Prognostic nutritional index.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) and prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts chemotherapy response and prognosis in locally advanced gastric cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy with PD-1 antibody sintilimab and XELOX: a prospective study.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Mar 14;22(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02199-9. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35287591 Free PMC article.
-
Combined systemic inflammatory immune index and prognostic nutrition index as chemosensitivity and prognostic markers for locally advanced gastric cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a retrospective study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Aug 15;24(1):1014. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12771-z. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39148031 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Inflammatory biomarker correlations and prognosis in high-risk gastrointestinal stromal tumor patients: a multicenter retrospective analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Feb 26;25(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03710-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40011800 Free PMC article.
-
Open transanal resection of low rectal stromal tumor following neoadjuvant therapy of imatinib mesylate: Report of 11 cases and review of literature.Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jun;16(3):123-128. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13292. Epub 2020 Jan 19. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31957191 Review.
-
Adjuvant and neoadjuvant imatinib therapy: current role in the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors.Int J Cancer. 2011 Dec 1;129(11):2533-42. doi: 10.1002/ijc.26234. Int J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21671474 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of first‑line therapies in patients with locally advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors with KIT and PDGFRα gene mutations: A single‑center study.Oncol Lett. 2025 Apr 14;29(6):299. doi: 10.3892/ol.2025.15045. eCollection 2025 Jun. Oncol Lett. 2025. PMID: 40276085 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index and prognostic nutrition index in patients with epithelial ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2025 Mar 7;18(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s13048-025-01631-4. J Ovarian Res. 2025. PMID: 40055764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of the Advanced Lung Cancer Inflammation Index (ALI) and Gustave Roussy Immune (GRIm) score with immune checkpoint inhibitor efficacy in patients with gastrointestinal and lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2024 Apr 8;24(1):428. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-12149-1. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38589844 Free PMC article.
-
Potential biomarkers for the prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Apr 15;17(4):102831. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i4.102831. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40235893 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive value of D-dimer combined with systemic immune-inflammation index for the presence of pulmonary thromboembolism in AECOPD patients.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Aug 1;12:1582913. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1582913. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40823589 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maki RG, Blay JY, Demetri GD, Fletcher JA, Joensuu H, Martín-Broto J, Nishida T, Reichardt P, Schöffski P, Trent JC. Key issues in the clinical management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors: an expert discussion. Oncologist. 2015;20(7):823–830. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0471. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

