Exosomal transmission of viruses, a two-edged biological sword
- PMID: 36691072
- PMCID: PMC9868521
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-022-01037-5
Exosomal transmission of viruses, a two-edged biological sword
Abstract
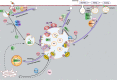
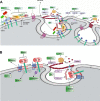
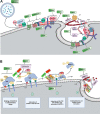
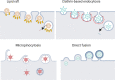
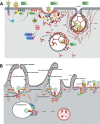
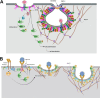
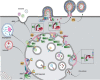
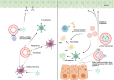
As a common belief, most viruses can egress from the host cells as single particles and transmit to uninfected cells. Emerging data have revealed en bloc viral transmission as lipid bilayer-cloaked particles via extracellular vesicles especially exosomes (Exo). The supporting membrane can be originated from multivesicular bodies during intra-luminal vesicle formation and autophagic response. Exo are nano-sized particles, ranging from 40-200 nm, with the ability to harbor several types of signaling molecules from donor to acceptor cells in a paracrine manner, resulting in the modulation of specific signaling reactions in target cells. The phenomenon of Exo biogenesis consists of multiple and complex biological steps with the participation of diverse constituents and molecular pathways. Due to similarities between Exo biogenesis and virus replication and the existence of shared pathways, it is thought that viruses can hijack the Exo biogenesis machinery to spread and evade immune cells. To this end, Exo can transmit complete virions (as single units or aggregates), separate viral components, and naked genetic materials. The current review article aims to scrutinize challenges and opportunities related to the exosomal delivery of viruses in terms of viral infections and public health. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Exosomes; Infection; Shared signaling pathways; Transmission; Viruses.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare there is no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Viral Proteins in the Regulation of Exosomes Biogenesis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 May 13;11:671625. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.671625. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34055668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Infectious Unit: Extracellular Vesicles Carrying Virus Populations.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 6;37:171-197. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-040621-032416. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34270326
-
[Exosomes: another arena for the game between viruses and hosts].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020 Sep 25;36(9):1732-1740. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200039. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 33164452 Review. Chinese.
-
Extracellular vesicles: Vehicles of en bloc viral transmission.Virus Res. 2019 May;265:143-149. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2019.03.023. Epub 2019 Mar 27. Virus Res. 2019. PMID: 30928427 Review.
-
[Exosomes in the life cycle of viruses and the pathogenesis of viral infections].Vopr Virusol. 2023 Jul 6;68(3):181-197. doi: 10.36233/0507-4088-173. Vopr Virusol. 2023. PMID: 37436410 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Mode of Viral Propagation Exploited by Enveloped and Non-Enveloped Viruses.Microorganisms. 2024 Jan 28;12(2):274. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12020274. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38399678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective pharmacological inhibition alters human carcinoma lung cell-derived extracellular vesicle formation.Heliyon. 2023 May 30;9(6):e16655. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16655. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37303541 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial and challenges of exosome application in ischemic heart disease.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 May 19;16(1):247. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04363-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40390086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current updates on the molecular and genetic signals as diagnostic and therapeutic targets for hepatitis B virus-associated hepatic malignancy.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 8;10(14):e34288. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34288. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39100497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Droplets: Formation, Degradation, and Their Role in Cellular Responses to Flavivirus Infections.Microorganisms. 2024 Mar 24;12(4):647. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12040647. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38674592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chan M-H, Chang Z-X, Huang C-YF, Lee LJ, Liu R-S, Hsiao M. Integrated therapy platform of exosomal system: hybrid inorganic/organic nanoparticles with exosomes for cancer treatment. Nanoscale Horizons; 2022. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

