The effects of psychosocial and economic factors on the quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease and their caregivers in Klang Valley, Malaysia: protocol for a mixed-methods study
- PMID: 36691236
- PMCID: PMC9171257
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-059305
The effects of psychosocial and economic factors on the quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease and their caregivers in Klang Valley, Malaysia: protocol for a mixed-methods study
Abstract
Introduction: The number of patients in Malaysia requiring dialysis is expected to rise substantially in the future due to the ageing population and increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus and hypertension. Hence, more individuals will be expected to adopt the role of caregivers in the future. The upward trend of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and caregiving for dialysis patients has detrimental consequences for both patients and caregivers in terms of their psychological well-being and quality of life. Despite the current circumstances, there are very few studies in Malaysia that have explored the psychosocial factors, specifically on the economic impact of the management of ESRD.
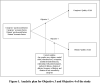
Methods and analysis: This two-phase sequential explanatory mixed-methods design, incorporating a quantitative design (phase I) and a qualitative study (phase II), is to be conducted in 4 government hospitals and 10 other non-governmental organisations or private dialysis centres within Klang Valley, Malaysia. A cross-sectional survey (phase I) will include 236 patient-caregiver dyads, while focus group discussions (phase II) will include 30 participants. The participants for both phases will be recruited purposively. Descriptive statistics, independent sample t-tests and multiple regression analysis will be used for analyses in phase I, and thematic analysis will be used in phase II.
Ethics and dissemination: Approval for the study has been obtained from the National Medical Research and Ethics Committee (MREC) (NMRR-21-1012-59714) and the Research Ethics Committee of Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz UKM (UKM PPI/111/8/JEP-2021-078) and University of Malaya Medical Centre (MREC ID NO: 2 02 178-10346). Informed consent of the participants will be obtained beforehand, and no personal identifiers will be obtained from the participants to protect their anonymity. The findings will be published in peer-reviewed scientific journals and presented at national or international conferences with minimal anonymised data.
Keywords: Adult nephrology; Chronic renal failure; Dialysis; End stage renal failure; MENTAL HEALTH.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biopsychosocial approach to understanding predictors of depressive symptoms among men who have sex with men living with HIV in Selangor, Malaysia: A mixed methods study protocol.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 2;18(6):e0286816. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286816. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37267403 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment decision-making and care among older adults with kidney failure: protocol for a multicentre, prospective observational cohort study with nested substudies and linked qualitative research (the Elderly Advanced CKD Programme).BMJ Open. 2022 Dec 29;12(12):e066156. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-066156. BMJ Open. 2022. PMID: 36581411 Free PMC article.
-
Protocol of a mixed method, randomized controlled study to assess the efficacy of a psychosocial intervention to reduce fatigue in patients with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD).BMC Nephrol. 2016 Jul 8;17(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0277-8. BMC Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27391406 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Appendix to dialysis centre guidelines: recommendations for the relationship between outpatient haemodialysis centres and reference hospitals. Opinions from the Outpatient Dialysis Group. Grupo de Trabajo de Hemodiálisis Extrahospitalaria.Nefrologia. 2011;31(6):664-9. doi: 10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2011.Oct.11001. Nefrologia. 2011. PMID: 22130281 English, Spanish.
-
Psychosocial interventions for preventing and treating depression in dialysis patients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Dec 2;12(12):CD004542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004542.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 31789430 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Self-Reported Socio-Economic and Psychological Burdens for Caregivers of Patients Undergoing Dialysis: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2025 Mar 10;17(3):e80353. doi: 10.7759/cureus.80353. eCollection 2025 Mar. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40213708 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Life of Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease Under Maintenance Hemodialysis and Their Caregivers: A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2023 Oct 7;15(10):e46651. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46651. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37936999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nephrology Services and Department of Public Health Mustapha FI, Bavanandan S, eds. National action plan for healthy kidneys (ACT-KID): medium term strategic plan to reduce the burden of chronic kidney disease in Malaysia (2018-2025). Putrajaya: Ministry of Health Malaysia, 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
