Acteoside alleviates UUO-induced inflammation and fibrosis by regulating the HMGN1/TLR4/TREM1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 36691481
- PMCID: PMC9864189
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.14765
Acteoside alleviates UUO-induced inflammation and fibrosis by regulating the HMGN1/TLR4/TREM1 signaling pathway
Abstract
Purpose: Acteoside (Act), a phenylethanoid compound that was first isolated from mullein, has been widely used for the investigation of anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effect. However, the mechanism of Act against unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-mediated renal injury is largely unknown. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the effects of Act on UUO rats and possible mechanisms.
Methods: A total of 20 Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were divided randomly into three groups (n ≥ 6): (i) sham-operated group (Sham); (ii) UUO group (UUO+Saline); and (iii) UUO + Act 40 mg/kg/day, (UUO+Act); Continuous gavage administration for 2 weeks postoperatively, while the rats in Sham and UUO+saline groups were given equal amounts of saline. All rats were sacrificed after 14 days, the urine and blood samples were collected for biochemical analysis, the renal tissues were collected for pathological staining and immunohistochemistry. Correlations between individual proteins were analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis.
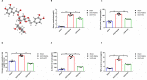
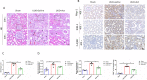
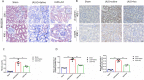
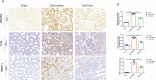
Results: The results of renal function indexes and histopathological staining showed that Act could improve renal function by reducing serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen and urine protein at the same time, Act could alleviate renal inflammation and fibrosis. In addition, the results of immunohistochemistry showed that Act could reduce the expression of inflammation and kidney injury-related proteins F4/80, Mcp-1, KIM-1 proteins, as well as the expression of fibrosis-related protein α-SMA and β-catenin. More importantly, Act can also reduce the expression of HMGN1, TLR4 and TREM-1 proteins.
Conclusion: These data demonstrate that Act can ameliorate UUO-induced renal inflammation and fibrosis in rats probably through triggering HMGN1/TLR4/TREM-1 pathway.
Keywords: Acteoside; HMGN1; Inflammation; Obstructive nephropathy; Renal fibrosis.
©2023 Mao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-renal fibrosis effect of asperulosidic acid via TGF-β1/smad2/smad3 and NF-κB signaling pathways in a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction.Phytomedicine. 2019 Feb;53:274-285. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30668407
-
Puerarin Alleviates UUO-Induced Inflammation and Fibrosis by Regulating the NF-κB P65/STAT3 and TGFβ1/Smads Signaling Pathways.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Aug 24;15:3697-3708. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S321879. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34465981 Free PMC article.
-
[A Study on the Role and Mechanism of Fenofibrate in Mice Renal Fibrosis Induced by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 Sep;51(5):670-674. doi: 10.12182/20200960206. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 32975082 Chinese.
-
LncRNA Meg3 Aggravates Renal Fibrosis Caused by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Rats by Activating the Hedgehog Pathway.Discov Med. 2024 Mar;36(182):604-612. doi: 10.24976/Discov.Med.202436182.57. Discov Med. 2024. PMID: 38531801
-
Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium attenuates renal fibrosis by reducing inflammation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Jan 12;9(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0760-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29329595 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Verbascoside restores gastrointestinal integrity and attenuates inflammation in a rat model of 5-FU-induced mucositis.Med Oncol. 2025 Jun 16;42(7):267. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02823-0. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40524059 Free PMC article.
-
Role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 in kidney diseases: A biomarker and potential therapeutic target.Chin Med J (Engl). 2024 Jul 20;137(14):1663-1673. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000003197. Epub 2024 May 28. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024. PMID: 38809056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acteoside-containing caffeic acid is bioactive functional group of antifibrotic effect by suppressing inflammation via inhibiting AHR nuclear translocation in chronic kidney disease.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 Jun 20. doi: 10.1038/s41401-025-01598-4. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 40542283
-
Acteoside as a multifunctional natural glycoside: therapeutic potential across various diseases.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jun 23. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01811-0. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40549319 Review.
-
Renal-Protective Roles of Lipoic Acid in Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 1;15(7):1732. doi: 10.3390/nu15071732. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049574 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

