Natural immunity stimulation using ELICE16INDURES® plant conditioner in field culture of soybean
- PMID: 36691550
- PMCID: PMC9860300
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12907
Natural immunity stimulation using ELICE16INDURES® plant conditioner in field culture of soybean
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Natural immunity stimulation using ELICE16INDURES® plant conditioner in field culture of soybean" [Heliyon 9 (1), (January 2023) Article e12907].Heliyon. 2023 Feb 25;9(3):e13954. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13954. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37101488 Free PMC article.
Abstract
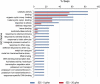
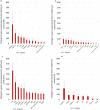
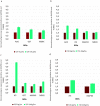
Recently, climate change has had an increasing impact on the world. Innate defense mechanisms operating in plants - such as PAMP-triggered Immunity (PTI) - help to reduce the adverse effects caused by various abiotic and biotic stressors. In this study, the effects of ELICE16INDURES® plant conditioner for organic farming, developed by the Research Institute for Medicinal Plants and Herbs Ltd. Budakalász Hungary, were studied in a soybean population in Northern Hungary. The active compounds and ingredients of this product were selected in such a way as to facilitate the triggering of general plant immunity without the presence and harmful effects of pathogens, thereby strengthening the healthy plant population and preparing it for possible stress effects. In practice, treatments of this agent were applied at two different time points and two concentrations. The conditioning effect was well demonstrated by using agro-drone and ENDVI determination in the soybean field. The genetic background of healthier plants was investigated by NGS sequencing, and by the expression levels of genes encoding enzymes involved in the catalysis of metabolic pathways regulating PTI. The genome-wide transcriptional profiling resulted in 13 contigs related to PAMP-triggered immunity and activated as a result of the treatments. Further analyses showed 16 additional PTI-related contigs whose gene expression changed positively as a result of the treatments. The gene expression values of genes encoded in these contigs were determined by in silico mRNA quantification and validated by RT-qPCR. Both - relatively low and high treatments - showed an increase in gene expression of key genes involving AOC, IFS, MAPK4, MEKK, and GST. Transcriptomic results indicated that the biosyntheses of jasmonic acid (JA), salicylic acid (SA), phenylpropanoid, flavonoid, phytoalexin, and cellular detoxification processes were triggered in the appropriate molecular steps and suggested that plant immune reactions may be activated also artificially, and innate immunity can be enhanced with proper plant biostimulants.
Keywords: Defense mechanism; ELICE16INDURES®; Expression profiling; Glycine max; Soybean.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
RNA-seq datasets of field soybean cultures conditioned by Elice16Indures® biostimulator.Data Brief. 2022 Apr 13;42:108182. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108182. eCollection 2022 Jun. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 35496495 Free PMC article.
-
Dataset of conditioning effect of herbal extract-based plant biostimulants in pea (Pisum sativum).Data Brief. 2022 Dec 5;46:108800. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108800. eCollection 2023 Feb. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 36569538 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of microbial bio-agents as elicitors in plant defense mechanism under biotic stress: A review.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2021 Aug 8;2:100054. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100054. eCollection 2021 Dec. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2021. PMID: 34841345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insight into melatonin-mediated response and signaling in the regulation of plant defense under biotic stress.Plant Mol Biol. 2022 Jul;109(4-5):385-399. doi: 10.1007/s11103-021-01202-3. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Plant Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34783977 Review.
-
Interactive regulation of immune-related resistance genes with salicylic acid and jasmonic acid signaling in systemic acquired resistance in the Xanthomonas-Brassica pathosystem.J Plant Physiol. 2024 Nov;302:154323. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2024.154323. Epub 2024 Aug 2. J Plant Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39106735
Cited by
-
'Garlic-lipo'4Plants: Liposome-Encapsulated Garlic Extract Stimulates ABA Pathway and PR Genes in Wheat (Triticum aestivum).Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 7;12(4):743. doi: 10.3390/plants12040743. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840091 Free PMC article.
-
Rhamnolipid-Enriched PA3 Fraction from Pseudomonas aeruginosa SWUC02 Primes Chili Plant Defense Against Anthracnose.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 23;25(23):12593. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312593. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684305 Free PMC article.
-
Supplementation of the Plant Conditioner ELICE Vakcina® Product with β-Aminobutyric Acid and Salicylic Acid May Lead to Trans-Priming Signaling in Barley (Hordeum vulgare).Plants (Basel). 2023 Jun 14;12(12):2308. doi: 10.3390/plants12122308. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375933 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szatmari A., et al. Characterisation of basal resistance (BR) by expression patterns of newly isolated representative genes in tobacco. Plant Cell Rep. 2006;25(7):728–740. - PubMed
-
- Jones J.D., Dangl J.L. The plant immune system. Nature. 2006;444(7117):323–329. - PubMed
-
- Cohn J., Sessa G., Martin G.B. Innate immunity in plants. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2001;13(1):55–62. - PubMed
-
- Amari K., Niehl A. Nucleic acid-mediated PAMP-triggered immunity in plants. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2020;42:32–39. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

