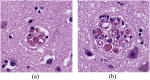
On the regional distribution of cerebral microvascular 'raspberries' and their association with cerebral atherosclerosis and acute circulatory failure
- PMID: 36691600
- PMCID: PMC9860404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cccb.2023.100157
On the regional distribution of cerebral microvascular 'raspberries' and their association with cerebral atherosclerosis and acute circulatory failure
Abstract
Introduction: In this follow-up study, cerebral microvascular formations termed 'raspberries' were quantified according to cerebral atherosclerosis (C-ASCL) and acute circulatory failure (ACF). We also examined the regional distribution of raspberries throughout the brain.
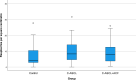
Materials and methods: The study population consisted of adult individuals who had undergone a diagnostic neuropathological autopsy. Groups were formed to examine the association between raspberries, C-ASCL and ACF (control group, C-ASCL group, C-ASCL+ACF group [n = 47 per group] and a combined C-ASCL-tot group [n = 94]). To examine the regional distribution, additional groups were formed based on previously known raspberry densities of the frontal cortex (high-, medium- and low-density group [n = 6 per group]). Raspberries were quantified on scanned haematoxylin-eosin-stained sections.
Results: Cortical raspberry density did not differ at a statistically significant level between the control group, the C-ASCL group and the C-ASCL+ACF group (P = 0.10) but did so between the control group and the C-ASCL-tot group (P = 0.033). The total raspberry density of the high-, medium- and low-density groups differed at a statistically significant level (P = 0.005), which remained in group-to-group comparisons of the high- and medium-density groups (P = 0.015) and the high- and low-density groups (P = 0.002). Raspberries were rare in cerebral white matter and in the cerebellum.
Conclusion: An association between raspberry density and C-ASCL is supported but is weaker than previously indicated. An association with ACF is not indicated. The raspberry density of the frontal cortex provides an approximation of the brain's total raspberry density.
Keywords: ACF, acute circulatory failure; Arteriosclerosis; C-ASCL, cerebral atherosclerosis; Cerebral ischemia; Cerebrovascular disease.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cortical microvascular raspberries and ageing: an independent but not exclusive relationship.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Dec 12;11(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01700-z. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 38087325 Free PMC article.
-
Increased frontocortical microvascular raspberry density in frontotemporal lobar degeneration compared to Lewy body disease and control cases: a neuropathological study.Free Neuropathol. 2025 Mar 4;6:7. doi: 10.17879/freeneuropathology-2025-6178. eCollection 2025 Jan. Free Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 40052111 Free PMC article.
-
Are cortical microvascular raspberries caused by cerebral hypoperfusion? An exploratory pathological study.Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2021 Aug 17;2:100026. doi: 10.1016/j.cccb.2021.100026. eCollection 2021. Cereb Circ Cogn Behav. 2021. PMID: 36324730 Free PMC article.
-
A cortical microvascular structure in vascular dementia, Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal lobar degeneration and nondemented controls: a sign of angiogenesis due to brain ischaemia?Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019 Oct;45(6):557-569. doi: 10.1111/nan.12552. Epub 2019 May 9. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30957900 Free PMC article.
-
Unexpected stability of aqueous dispersions of raspberry-like colloids.Nat Commun. 2018 Sep 6;9(1):3614. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05560-3. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30190497 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cortical microvascular raspberries and ageing: an independent but not exclusive relationship.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Dec 12;11(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01700-z. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 38087325 Free PMC article.
-
A neuropathologic feature of brain aging: multi-lumen vascular profiles.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Aug 28;11(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01638-2. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 37641147 Free PMC article.
-
Increased frontocortical microvascular raspberry density in frontotemporal lobar degeneration compared to Lewy body disease and control cases: a neuropathological study.Free Neuropathol. 2025 Mar 4;6:7. doi: 10.17879/freeneuropathology-2025-6178. eCollection 2025 Jan. Free Neuropathol. 2025. PMID: 40052111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hartmann P., Ramseier A., Gudat F., Mihatsch M.J., Polasek W. [Normal weight of the brain in adults in relation to age, sex, body height and weight] Pathologe. 1994;15(3):165–170. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources