Do Tobacco Companies Have an Incentive to Promote "Harm Reduction" Products?: The Role of Competition
- PMID: 36692328
- PMCID: PMC10664083
- DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntad014
Do Tobacco Companies Have an Incentive to Promote "Harm Reduction" Products?: The Role of Competition
Abstract
Introduction: Some cigarette companies have started to talk about replacing cigarettes with less harmful alternatives, which might include nicotine vaping products (NVPs), heated tobacco products (HTPs), and oral nicotine delivery products. We consider market competition as a primary driver of whether cigarette companies follow through on their stated intentions.
Aims and methods: We focus on the behavior of cigarette companies in the United States. We compare competition in the pre- and post-2012 time periods, analyze the impact of the growth in NVPs on smoking prevalence and cigarette company profits, and examine the potential future role of competition.
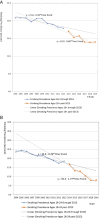
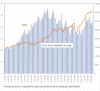
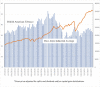
Results: Since 2006, consumers have broadened their use of non-combustible nicotine delivery products (NCNDPs) to include, inter alia, NVPs, HTPs, and oral nicotine pouches. U.S. cigarette companies have acquired major stakes in each of these product categories which corresponds to a period of rapidly declining adult smoking prevalence, especially among younger adults (ages 18-24 years). The shifting dynamics of the nicotine product marketplace are also reflected in cigarette company stock prices. While cigarette companies are likely to promote HTPs and nicotine delivery products over NVPs, their incentives will be directly related to competition from independent firms, which in turn will depend on government regulation.
Conclusions: Although cigarette companies will back alternatives to combusted tobacco when threatened by competition, the prospects for their lasting conversion to NCNDPs will depend on the extent of such competition, which will be influenced by government regulation of tobacco products.
Implications: Regulations that limit competition from independent firms while also protecting cigarette company profits risk slowing or even reversing recent declines in smoking, especially among youth and young adults. Regulations that reduce the appeal and addictiveness of combusted tobacco products, such as higher cigarette taxes or a reduced nicotine standard, will encourage smokers to quit and/or switch to less harmful non-combusted forms of tobacco. The regulation of non-combustible nicotine delivery products and cigarettes should be proportionate to their relative risks, so that smokers have incentives to switch from combustibles to safer alternatives, and cigarette companies have incentives to promote safer products.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco.
Conflict of interest statement
K. Michael Cummings has served as a paid expert witness in litigation against cigarette companies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Patterns of Non-Cigarette Tobacco and Nicotine Use Among Current Cigarette Smokers and Recent Quitters: Findings From the 2020 ITC Four Country Smoking and Vaping Survey.Nicotine Tob Res. 2021 Aug 18;23(9):1611-1616. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntab040. Nicotine Tob Res. 2021. PMID: 33693833 Free PMC article.
-
Characterizing Heated Tobacco Product Use Among Adult Cigarette Smokers and Nicotine Vaping Product Users in the 2018 ITC Four Country Smoking & Vaping Survey.Nicotine Tob Res. 2022 Mar 1;24(4):493-502. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntab217. Nicotine Tob Res. 2022. PMID: 34669964 Free PMC article.
-
A Decision-Theoretic Public Health Framework for Heated Tobacco and Nicotine Vaping Products.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 18;19(20):13431. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013431. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36294011 Free PMC article.
-
Public Health Policies on E-Cigarettes.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019 Aug 28;21(10):111. doi: 10.1007/s11886-019-1204-y. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31463564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiopulmonary Impact of Electronic Cigarettes and Vaping Products: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association.Circulation. 2023 Aug 22;148(8):703-728. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001160. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Circulation. 2023. PMID: 37458106 Review.
Cited by
-
How to Identify e-Cigarette Brands Available in the United States During 2020-2022: Development and Usability Study.JMIR Form Res. 2024 Feb 28;8:e47570. doi: 10.2196/47570. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 38416562 Free PMC article.
-
How cigarette excise tax pass-through to prices responds to the uptake and evolution of e-cigarettes (ECs).Tob Control. 2025 Jan 2;34(1):85-91. doi: 10.1136/tc-2023-058078. Tob Control. 2025. PMID: 37640531 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating trends in cigarette and HTP use in Japan and measurement issues in the National Health and Nutrition Survey.Tob Control. 2024 Jun 21:tc-2023-058526. doi: 10.1136/tc-2023-058526. Online ahead of print. Tob Control. 2024. PMID: 38906697
-
Subculture wars: The struggle for the vape industry.Br J Sociol. 2023 Jan;74(1):3-16. doi: 10.1111/1468-4446.12981. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Br J Sociol. 2023. PMID: 36329664 Free PMC article.
References
-
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Nicotine Addiction. A Report of the Surgeon General, 1988. Atlanta, GA: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; 1988.
-
- Slade J. Nicotine delivery devices. In: Orleans CT, Slade J, eds. Nicotine Addiction: Principles and Management. New York: Oxford University Press; 1993.
-
- Brandt A. The Cigarette Century: The Rise, Fall, and Deadly Persistence of the Product That Defined America. New York: Basic Books; 2007.
-
- Proctor R. Golden Holocaust: Origins of the Cigarette Catastrophe and the Case for Abolition. Berkeley: University of California Press; 2011.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

