Streptococcus dysgalactiae Bloodstream Infections, Norway, 1999-2021
- PMID: 36692331
- PMCID: PMC9881787
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2902.221218
Streptococcus dysgalactiae Bloodstream Infections, Norway, 1999-2021
Abstract
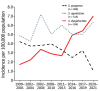
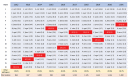
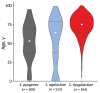
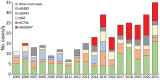
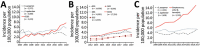
Streptococcus dysgalactiae increasingly is recognized as a pathogen of concern for human health. However, longitudinal surveillance data describing temporal trends of S. dysgalactiae are scarce. We retrospectively identified all β-hemolytic streptococcal bloodstream infections reported in Bergen, in western Norway, during 1999-2021. To explore S. dysgalactiae disease burden in a broader context, we mapped the incidence of all microbial species causing bloodstream infections during 2012-2021. We found S. dysgalactiae incidence rates substantially increased during the study period; by 2021, S. dysgalactiae was the fifth most common pathogen causing bloodstream infections in our region. We noted genotypic shifts and found that the rising trend was related in part to the introduction and expansion of the stG62647 emm-type. S. dysgalactiae is among the most common causes of bloodstream infections in western Norway, and increased surveillance and unambiguous species identification are needed to monitor the disease burden attributable to this pathogen.
Keywords: Norway; Streptococcus dysgalactiae; bacteria; beta-hemolytic streptococcus; bloodstream infections; epidemiology; incidence rates; streptococci.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Temporal trends of β-haemolytic streptococcal osteoarticular infections in western Norway.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Oct 4;16(1):535. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1874-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27716100 Free PMC article.
-
Beta-haemolytic group A, C and G streptococcal infections in Western Norway: a 15-year retrospective survey.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015 Feb;21(2):171-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2014.08.019. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015. PMID: 25658557
-
Necrotizing soft tissue infections caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis of groups C and G in western Norway.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013 Dec;19(12):E545-50. doi: 10.1111/1469-0691.12276. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013. PMID: 23795951
-
Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis bacteremia: an emerging infection.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014 Aug;33(8):1303-10. doi: 10.1007/s10096-014-2092-0. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 24682845 Review.
-
Intra-familial transmission of Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. equisimilis (SDSE): A first case report and review of the literature.J Infect Chemother. 2022 Jun;28(6):819-822. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2022.01.017. Epub 2022 Feb 1. J Infect Chemother. 2022. PMID: 35115237 Review.
Cited by
-
Case Report: Streptococcus dysgalactiae ssp. dysgalactiae bloodstream infections in patients with breast cancer after radiotherapy and chemotherapy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 30;12:1572998. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1572998. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40520780 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive streptococcus dysgalactiae endocarditis with extensive multiorgan involvement.Oxf Med Case Reports. 2025 May 28;2025(5):omaf053. doi: 10.1093/omcr/omaf053. eCollection 2025 May. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2025. PMID: 40443848 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiological and microbial trends of infective endocarditis in western Norway: a 7-year prospective observational study.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Jul 17;24(1):702. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09596-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39020296 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Aspects and Disease Severity of Streptococcus dysgalactiae Subspecies equisimilis Bacteremia, Finland1.Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Sep;30(9):1770-1778. doi: 10.3201/eid3009.240278. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39173664 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus dysgalactiae subspecies equisimilis household transmission and mobile genetic element exchange.Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 24;15(1):3477. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47816-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38658529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Active bacterial core surveillance [cited 2022 Nov 16]. www.cdc.gov/abcs/reports-findings/surv-reports.html
-
- Australian Government, Department of Health and Aged Care. Australian national notifiable diseases case definition [cited 2022 Nov 16]. https://www.health.gov.au/resources/publications/invasive-group-a-strept...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

