Increasing liver stiffness is associated with higher incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C infection and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-A population-based study
- PMID: 36693057
- PMCID: PMC9873178
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280647
Increasing liver stiffness is associated with higher incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C infection and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-A population-based study
Abstract
Background & aims: Both non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection commonly result in hepatic fibrosis and may lead to cirrhosis. This study aims to determine the incidence of HCC in patients with HCV or NAFLD complicated by advanced fibrosis, inferred from measurements of liver stiffness.
Methods: Using Veterans Affairs (VA) Informatics and Computing Infrastructure (VINCI), we identified a nationwide cohort of patients with an existing diagnosis of HCV or NAFLD with liver transient elastography (TE) testing from 2015 to 2019. HCC cases, along with a random sample of non-HCC patients, were identified and validated, leading to calculation of incidence rates for HCC after adjustment for confounders.
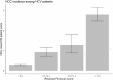
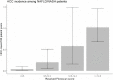
Results: 26,161 patients carried a diagnosis of HCV and 13,629 were diagnosed with NAFLD at the time of testing. In those with HCV, rates of HCC increased with liver stiffness with incidences of 0.28 (95% CI 0.24, 0.34), 0.93 (95% CI 0.72, 1.17), 1.28 (95% CI 0.89, 1.79), and 2.79 (95% CI 2.47, 3.14)/100,000 person years for TE score ranges <9.5 kPa, 9.5-12.5 kPa, 12.5-14.5 kPa and >14.5 kPa, respectively, after a median follow-up of 2.3 years. HCC incidence also increased with higher TE liver stiffness measures in NAFLD after a median follow-up of 1.1 years.
Conclusion: In this retrospective cohort, the incidence of HCC in HCV and NAFLD increases with higher TE liver stiffness measures, confirming that advanced fibrosis portends risk in viral and non-viral fibrotic liver diseases. Additional comparative studies are needed to determine the optimal cut point of TE liver stiffness to inform HCC screening guidelines and approaches.
Copyright: This is an open access article, free of all copyright, and may be freely reproduced, distributed, transmitted, modified, built upon, or otherwise used by anyone for any lawful purpose. The work is made available under the Creative Commons CC0 public domain dedication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer. Updated September 12, 2018. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer. Accessed November 27, 2020.
-
- Wild CP, Weiderpass E, Stewart BW, eds. World cancer report: cancer research for cancer prevention. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical