METTL3 is essential for normal progesterone signaling during embryo implantation via m6A-mediated translation control of progesterone receptor
- PMID: 36693099
- PMCID: PMC9945998
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2214684120
METTL3 is essential for normal progesterone signaling during embryo implantation via m6A-mediated translation control of progesterone receptor
Abstract
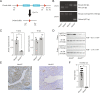
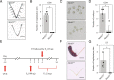
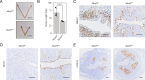
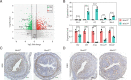
Embryo implantation, a crucial step in human reproduction, is tightly controlled by estrogen and progesterone (P4) via estrogen receptor alpha and progesterone receptor (PGR), respectively. Here, we report that N6-methyladenosine (m6A), the most abundant mRNA modification in eukaryotes, plays an essential role in embryo implantation through the maintenance of P4 signaling. Conditional deletion of methyltransferase-like 3 (Mettl3), encoding the m6A writer METTL3, in the female reproductive tract using a Cre mouse line with Pgr promoter (Pgr-Cre) resulted in complete implantation failure due to pre-implantation embryo loss and defective uterine receptivity. Moreover, the uterus of Mettl3 null mice failed to respond to artificial decidualization. We further found that Mettl3 deletion was accompanied by a marked decrease in PGR protein expression. Mechanistically, we found that Pgr mRNA is a direct target for METTL3-mediated m6A modification. A luciferase assay revealed that the m6A modification in the 5' untranslated region (5'-UTR) of Pgr mRNA enhances PGR protein translation efficiency in a YTHDF1-dependent manner. Finally, we demonstrated that METTL3 is required for human endometrial stromal cell decidualization in vitro and that the METTL3-PGR axis is conserved between mice and humans. In summary, this study provides evidence that METTL3 is essential for normal P4 signaling during embryo implantation via m6A-mediated translation control of Pgr mRNA.
Keywords: METTL3; embryo implantation; m6A; progesterone receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

