Genomic Complexity Predicts Resistance to Endocrine Therapy and CDK4/6 Inhibition in Hormone Receptor-Positive (HR+)/HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
- PMID: 36693175
- PMCID: PMC10150240
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-2177
Genomic Complexity Predicts Resistance to Endocrine Therapy and CDK4/6 Inhibition in Hormone Receptor-Positive (HR+)/HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Clinical biomarkers to identify patients unlikely to benefit from CDK4/6 inhibition (CDK4/6i) in combination with endocrine therapy (ET) are lacking. We implemented a comprehensive circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis to identify genomic features for predicting and monitoring treatment resistance.
Experimental design: ctDNA was isolated from 216 plasma samples collected from 51 patients with hormone receptor-positive (HR+)/HER2-negative (HER2-) metastatic breast cancer (MBC) on a phase II trial of palbociclib combined with letrozole or fulvestrant (NCT03007979). Boosted whole-exome sequencing (WES) was performed at baseline and clinical progression to evaluate genomic alterations, mutational signatures, and blood tumor mutational burden (bTMB). Low-pass whole-genome sequencing was performed at baseline and serial timepoints to assess blood copy-number burden (bCNB).
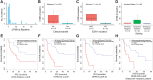
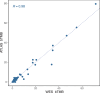
Results: High bTMB and bCNB were associated with lack of clinical benefit and significantly shorter progression-free survival (PFS) compared with patients with low bTMB or low bCNB (all P < 0.05). Dominant APOBEC signatures were detected at baseline exclusively in cases with high bTMB (5/13, 38.5%) versus low bTMB (0/37, 0%; P = 0.0006). Alterations in ESR1 were enriched in samples with high bTMB (P = 0.0005). There was a high correlation between bTMB determined by WES and bTMB determined using a 600-gene panel (R = 0.98). During serial monitoring, an increase in bCNB score preceded radiographic progression in 12 of 18 (66.7%) patients.
Conclusions: Genomic complexity detected by noninvasive profiling of bTMB and bCNB predicted poor outcomes in patients treated with ET and CDK4/6i and identified early disease progression before imaging. Novel treatment strategies including immunotherapy-based combinations should be investigated in this population.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures




Comment in
- 1078-0432. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-29-9-HI
Similar articles
-
Extended follow-up of palbociclib with fulvestrant or letrozole for endocrine-sensitive, hormone receptor-positive/HER2-negative advanced breast cancer in the PARSIFAL trial.ESMO Open. 2025 Jul;10(7):105309. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2025.105309. Epub 2025 Jun 17. ESMO Open. 2025. PMID: 40532361 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Abemaciclib Plus Fulvestrant in Advanced Breast Cancer After Progression on CDK4/6 Inhibition: Results From the Phase III postMONARCH Trial.J Clin Oncol. 2025 Mar 20;43(9):1101-1112. doi: 10.1200/JCO-24-02086. Epub 2024 Dec 18. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39693591 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Survival Following CDK4/6 Inhibitor Therapy for Hormone Receptor-Positive, ERBB2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer.JAMA Netw Open. 2025 Feb 3;8(2):e2461067. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.61067. JAMA Netw Open. 2025. PMID: 39982725 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of CDK4/6 inhibitors in HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Curr Med Res Opin. 2024 Oct;40(10):1753-1767. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2024.2402074. Epub 2024 Sep 21. Curr Med Res Opin. 2024. PMID: 39305463
-
Influence of ethnicity on cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor efficacy and toxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast. 2025 Feb;79:103833. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2024.103833. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Breast. 2025. PMID: 39579620 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sex differences in renal cell carcinoma: a single-cell analysis reveals exhausted CD8+ T-cells highly infiltrated in males.Biol Sex Differ. 2023 Sep 15;14(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00540-9. Biol Sex Differ. 2023. PMID: 37715192 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid biopsy: Cell-free DNA based analysis in breast cancer.J Liq Biopsy. 2023 Jul 27;1:100002. doi: 10.1016/j.jlb.2023.100002. eCollection 2023 Sep. J Liq Biopsy. 2023. PMID: 40027284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elacestrant in ER+, HER2- Metastatic Breast Cancer with ESR1-Mutated Tumors: Subgroup Analyses from the Phase III EMERALD Trial by Prior Duration of Endocrine Therapy plus CDK4/6 Inhibitor and in Clinical Subgroups.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 1;30(19):4299-4309. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-24-1073. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39087959 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical impact of single-gene vs. panel sequencing in advanced HR + /HER2- breast cancer: insights and implications.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2025 Aug 7;11(1):86. doi: 10.1038/s41523-025-00805-z. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40775238 Free PMC article.
-
From Detection to Cure - Emerging Roles for Urinary Tumor DNA (utDNA) in Bladder Cancer.Curr Oncol Rep. 2024 Aug;26(8):945-958. doi: 10.1007/s11912-024-01555-0. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Curr Oncol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38837106 Review.
References
-
- Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J, Inoue K, Pivot X, et al. . The effect of abemaciclib plus fulvestrant on overall survival in hormone receptor-positive, ERBB2-negative breast cancer that progressed on endocrine therapy-MONARCH 2: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 2020;6:116–24. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giuliano M, Schettini F, Rognoni C, Milani M, Jerusalem G, Bachelot T, et al. . Endocrine treatment versus chemotherapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 2019;20:1360–9. - PubMed
-
- Turner NC, Slamon DJ, Ro J, Bondarenko I, Im SA, Masuda N, et al. . Overall survival with palbociclib and fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2018;379:1926–36. - PubMed
-
- Im SA, Lu YS, Bardia A, Harbeck N, Colleoni M, Franke F, et al. . Overall survival with ribociclib plus endocrine therapy in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2019;381:307–16. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Fasching PA, De Laurentiis M, Im SA, et al. . Overall survival with ribociclib plus fulvestrant in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2020;382:514–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

