Deciphering the multi-scale, quantitative cis-regulatory code
- PMID: 36693380
- PMCID: PMC9898153
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.12.032
Deciphering the multi-scale, quantitative cis-regulatory code
Abstract
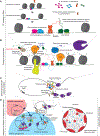
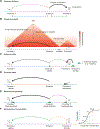
Uncovering the cis-regulatory code that governs when and how much each gene is transcribed in a given genome and cellular state remains a central goal of biology. Here, we discuss major layers of regulation that influence how transcriptional outputs are encoded by DNA sequence and cellular context. We first discuss how transcription factors bind specific DNA sequences in a dosage-dependent and cooperative manner and then proceed to the cofactors that facilitate transcription factor function and mediate the activity of modular cis-regulatory elements such as enhancers, silencers, and promoters. We then consider the complex and poorly understood interplay of these diverse elements within regulatory landscapes and its relationships with chromatin states and nuclear organization. We propose that a mechanistically informed, quantitative model of transcriptional regulation that integrates these multiple regulatory layers will be the key to ultimately cracking the cis-regulatory code.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II; activation domain; chromatin; cis-regulatory code; cis-regulatory element; coactivator; cofactor; corepressor; enhancer; gene regulation; insulator; nucleosome; pioneer factor; promoter; regulatory domain; repression domain; silencer; topologically associating domain; transcription; transcription factor.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests J.W. is paid scientific advisory board member at Camp4 and Paratus Sciences. J.W. is an advisory board member at Cell Press journals, including Cell, Molecular Cell, and Developmental Cell.
Figures