Recognizing risk factors associated with poor outcomes among patients with COVID-19
- PMID: 36693489
- PMCID: PMC9862711
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcad.2023.01.006
Recognizing risk factors associated with poor outcomes among patients with COVID-19
Abstract
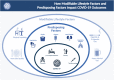
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has affected >610 million people globally, exerting major social, economic, and health impacts. Despite the large number of global casualities and severe symptomatology associated with COVID-19, a large number of individuals remain at elevated risk of infection and severe outcomes related to poor lifestyle behaviors and/or associated comorbidities. Beyond the well-known social distance and masking policies, maintaining an active lifestyle, minimizing the consumption of tobacco products, and maintaining an adequate nutrition status are some of the key factors that, in an affordable and accessible way, have the potential to improve health and minimize COVID-19 impact. In addition, bringing awareness of the higher risks and poor prognosis of COVID-19 when other conditions are present seems to be essential to protect those individuals with the highest risks.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cardiovascular disease; Physical activity; Risk factors; Sedentary behavior.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures

References
-
- Organization WH . 2022. WHO Coronavirus Dashboard.
-
- Services DoHaH . 2nd ed. 2023. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans - Executive Summary; pp. 1–7.
-
- Prevention CfDCa . Vol. 2022. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services; 2022. Physical Activity and COVID-19.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

