Recognizing the power of machine learning and other computational methods to accelerate progress in small molecule targeting of RNA
- PMID: 36693763
- PMCID: PMC10019373
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.079497.122
Recognizing the power of machine learning and other computational methods to accelerate progress in small molecule targeting of RNA
Abstract
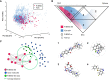
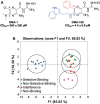
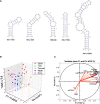
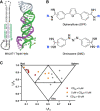
RNA structures regulate a wide range of processes in biology and disease, yet small molecule chemical probes or drugs that can modulate these functions are rare. Machine learning and other computational methods are well poised to fill gaps in knowledge and overcome the inherent challenges in RNA targeting, such as the dynamic nature of RNA and the difficulty of obtaining RNA high-resolution structures. Successful tools to date include principal component analysis, linear discriminate analysis, k-nearest neighbor, artificial neural networks, multiple linear regression, and many others. Employment of these tools has revealed critical factors for selective recognition in RNA:small molecule complexes, predictable differences in RNA- and protein-binding ligands, and quantitative structure activity relationships that allow the rational design of small molecules for a given RNA target. Herein we present our perspective on the value of using machine learning and other computation methods to advance RNA:small molecule targeting, including select examples and their validation as well as necessary and promising future directions that will be key to accelerate discoveries in this important field.
Keywords: RNA; cheminformatics; machine learning; pattern recognition; quantitative structure activity relationships; small molecule.
© 2023 Bagnolini et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
RNA-targeted small-molecule drug discoveries: a machine-learning perspective.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):384-397. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2223498. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37337437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecule-RNA targeting: starting with the fundamentals.Chem Commun (Camb). 2020 Nov 26;56(94):14744-14756. doi: 10.1039/d0cc06796b. Chem Commun (Camb). 2020. PMID: 33201954 Free PMC article.
-
R-BIND: An Interactive Database for Exploring and Developing RNA-Targeted Chemical Probes.ACS Chem Biol. 2019 Dec 20;14(12):2691-2700. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00631. Epub 2019 Oct 29. ACS Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31589399 Free PMC article.
-
A Machine Learning Method for RNA-Small Molecule Binding Preference Prediction.J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Oct 14;64(19):7386-7397. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01324. Epub 2024 Sep 12. J Chem Inf Model. 2024. PMID: 39265103
-
Machine Learning Methods for Small Data Challenges in Molecular Science.Chem Rev. 2023 Jul 12;123(13):8736-8780. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00189. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Chem Rev. 2023. PMID: 37384816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Recent trends in RNA informatics: a review of machine learning and deep learning for RNA secondary structure prediction and RNA drug discovery.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Jul 20;24(4):bbad186. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad186. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37232359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-targeted small-molecule drug discoveries: a machine-learning perspective.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):384-397. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2223498. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37337437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in machine-learning approaches to RNA-targeted drug design.Artif Intell Chem. 2024 Jun;2(1):100053. doi: 10.1016/j.aichem.2024.100053. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Artif Intell Chem. 2024. PMID: 38434217 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of RNA-Targeting Small Molecules: Challenges and Future Directions.MedComm (2020). 2025 Aug 24;6(9):e70342. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70342. eCollection 2025 Sep. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40859960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Binding free-energy landscapes of small molecule binder and non-binder to FMN riboswitch: All-atom molecular dynamics.Biophys Physicobiol. 2023 Dec 13;20(4):e200047. doi: 10.2142/biophysico.bppb-v20.0047. eCollection 2023. Biophys Physicobiol. 2023. PMID: 38344029 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
