Long-term statins administration exacerbates diabetic nephropathy via ectopic fat deposition in diabetic mice
- PMID: 36693830
- PMCID: PMC9873739
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-35944-z
Long-term statins administration exacerbates diabetic nephropathy via ectopic fat deposition in diabetic mice
Abstract
Statins play an important role in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Increasing attention has been given to the relationship between statins and insulin resistance, but many randomized controlled trials confirm that the therapeutic effects of statins on diabetic nephropathy are more beneficial than harmful. However, further confirmation of whether the beneficial effects of chronic statin administration on diabetic nephropathy outweigh the detrimental effects is urgently needed. Here, we find that long-term statin administration may increase insulin resistance, interfere with lipid metabolism, leads to inflammation and fibrosis, and ultimately fuel diabetic nephropathy progression in diabetic mice. Mechanistically, activation of insulin-regulated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway leads to increased fatty acid synthesis. Furthermore, statins administration increases lipid uptake and inhibits fatty acid oxidation, leading to lipid deposition. Here we show that long-term statins administration exacerbates diabetic nephropathy via ectopic fat deposition in diabetic mice.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

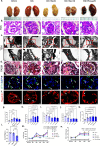

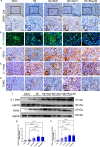
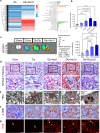

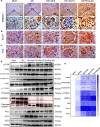



Comment in
-
The effect of long-term statin use on diabetic nephropathy.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023 Apr;19(4):189. doi: 10.1038/s41574-023-00813-8. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 36765197 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Liraglutide attenuates renal tubular ectopic lipid deposition in rats with diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting lipid synthesis and promoting lipolysis.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jun;156:104778. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104778. Epub 2020 Apr 2. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32247822
-
Disulfide-bond A oxidoreductase-like protein protects against ectopic fat deposition and lipid-related kidney damage in diabetic nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2019 Apr;95(4):880-895. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2018.10.038. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Kidney Int. 2019. PMID: 30791996
-
Efficacy of statins in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Lipids Health Dis. 2016 Oct 12;15(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0350-0. Lipids Health Dis. 2016. PMID: 27733168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NOD2 promotes renal injury by exacerbating inflammation and podocyte insulin resistance in diabetic nephropathy.Kidney Int. 2013 Aug;84(2):265-76. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.113. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Kidney Int. 2013. PMID: 23594678
-
Diabetic nephropathy. Its relationship to hypertension and means of pharmacological intervention.Drugs. 1997 Aug;54(2):197-234. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199754020-00002. Drugs. 1997. PMID: 9257079 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of hepatic and renal injury in lipid metabolism disorders in metabolic syndrome.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Sep 9;20(12):4783-4798. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.100394. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39309427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-omics characterization of diabetic nephropathy in the db/db mouse model of type 2 diabetes.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Jul 23;27:3399-3409. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.07.037. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40799908 Free PMC article.
-
N-p-coumaroyloctopamine ameliorates hepatic glucose metabolism and oxidative stress involved in a PI3K/AKT/GSK3β pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Apr 25;15:1396641. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1396641. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38725660 Free PMC article.
-
PCSK9 Inhibitors: A Potential Priority Choice for Lipid Management in Patients with Diabetic Kidney Disease.Drugs. 2025 Aug 14. doi: 10.1007/s40265-025-02221-w. Online ahead of print. Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40804212 Review.
-
Association between statin therapy and incident diabetes mellitus in patients with nephrotic syndrome: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Aug 26;26(1):490. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04424-5. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40859179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang L, et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016;375:905–906. - PubMed
-
- McGarry JD. Banting lecture 2001: dysregulation of fatty acid metabolism in the etiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2002;51:7–18. - PubMed
-
- Chen X, et al. Disulfide-bond A oxidoreductase-like protein protects against ectopic fat deposition and lipid-related kidney damage in diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2019;95:880–895. - PubMed
-
- DeFronzo RA, Reeves WB, Awad AS. Pathophysiology of diabetic kidney disease: impact of SGLT2 inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021;17:319–334. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

