A metabolic readout of the urine metabolome of COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 36694097
- PMCID: PMC9873393
- DOI: 10.1007/s11306-023-01971-6
A metabolic readout of the urine metabolome of COVID-19 patients
Abstract
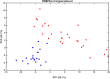
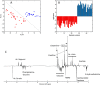
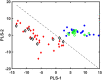
Analysis of urine samples from COVID-19 patients by 1H NMR reveals important metabolic alterations due to SAR-CoV-2 infection. Previous studies have identified biomarkers in urine that reflect metabolic alterations in COVID-19 patients. We have used 1H NMR to better define these metabolic alterations since this technique allows us to obtain a broad profile of the metabolites present in urine. This technique offers the advantage that sample preparation is very simple and gives us very complete information on the metabolites present. To detect these alterations, we have compared urine samples from COVID-19 patients (n = 35) with healthy people (n = 18). We used unsupervised (Robust PCA) and supervised (PLS-LDA) multivariate analysis methods to evaluate the differences between the two groups: COVID-19 and healthy controls. The differences focus on a group of metabolites related to energy metabolism (glucose, ketone bodies, glycine, creatinine, and citrate) and other processes related to bacterial flora (TMAO and formic acid) and detoxification (hippuric acid). The alterations in the urinary metabolome shown in this work indicate that SARS-CoV-2 causes a metabolic change from a normal situation of glucose consumption towards a gluconeogenic situation and possible insulin resistance.
Keywords: COVID-19; Gut microbiota; Human metabolism; Metabolomics.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diagnosis, Severity, and Prognosis from Potential Biomarkers of COVID-19 in Urine: A Review of Clinical and Omics Results.Metabolites. 2024 Dec 22;14(12):724. doi: 10.3390/metabo14120724. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39728505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic profiling of COVID-19 using serum and urine samples in intensive care and medical ward cohorts.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 10;14(1):23713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74641-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39390047 Free PMC article.
-
Longitudinal 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics in Saliva Unveils Signatures of Transition from Acute to Post-Acute Phase of SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Viruses. 2024 Nov 13;16(11):1769. doi: 10.3390/v16111769. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39599883 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding metabolic alterations after SARS-CoV-2 infection: insights from the patients' oral microenvironmental metabolites.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Jan 23;23(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07979-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36690957 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic characteristics and related pathways in patients with different severity of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Glob Health. 2025 Feb 28;15:04056. doi: 10.7189/jogh.15.04056. J Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40019163 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Time-series metabolomic profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection: Possible prognostic biomarkers in patients in the ICU by ¹H-NMR analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Jul 3;20(7):e0327244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0327244. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40608744 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis, Severity, and Prognosis from Potential Biomarkers of COVID-19 in Urine: A Review of Clinical and Omics Results.Metabolites. 2024 Dec 22;14(12):724. doi: 10.3390/metabo14120724. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39728505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathological Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2: A Review for Clinicians.Yale J Biol Med. 2024 Dec 19;97(4):431-445. doi: 10.59249/DQJH2274. eCollection 2024 Dec. Yale J Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39703609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic profiling of COVID-19 using serum and urine samples in intensive care and medical ward cohorts.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 10;14(1):23713. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74641-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39390047 Free PMC article.
-
Urine metabolomic analyses reveal metabolite disruptions in steroid hormone biosynthesis in monkeypox.iScience. 2025 Apr 29;28(6):112554. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112554. eCollection 2025 Jun 20. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40475255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bezabeh T, Capati A, Ijare OB. NMR-based urinary metabolomics applications. In: Gowda GAN, Raftery D, editors. Nmr-based metabolomics: methods and protocols. Springer; 2019. pp. 215–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
