A multidisciplinary approach to screen the post-COVID-19 conditions
- PMID: 36694110
- PMCID: PMC9872735
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-023-08006-4
A multidisciplinary approach to screen the post-COVID-19 conditions
Abstract
Background: Post-COronaVIrus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) conditions (PCC) include multiple symptoms afflicting different organs and systems. To evaluate the frequency and type of them, we described our multidisciplinary approach with preliminary results of the first enrolled patients.
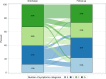
Methods: We included patients aged ≥ 18 years with hospital admission for confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection. Symptoms were grouped in five macro groups hereafter referred to as "Symptoms Category" (SC): respiratory SC (dyspnoea or cough), neurological SC (peripheral neuropathies, headache, impaired mobility, behavioural disorders), psychological SC (sleep disorders, mood disorders), muscular SC (arthromyalgia, asthenia), other SC (fever, alopecia, diarrhoea, weight loss, smell and taste alterations, sexual dysfunctions). SC were evaluated at discharge and at follow-up. Association between patients' characteristics and presence of SC at follow up was estimated by a logistic multivariable regression model.
Results: From June 2020 to July 2021, we followed up 361 patients: 128 (35.5%) who were previously admitted to Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and 233 patients to ordinary department. The median length of hospital stay was 20 days (Inter-Quartile-Range 13-32). Most patients (317/361, 87.8%) were still symptomatic at discharge, with one third referring three or more SC. At follow up, 67.3% (243/361) of patients still complained at least one SC. Moreover, 159 patients (44%) developed at least one new involved SC during follow up: 116 (72.9%) one SC, 39 (24.5%) two SC, 4 (2.5%) three or more SC. At follow up visit 130 of 361 (36%) were still with SC developed during follow up. At multivariable analysis presence of any SC at follow-up was associated with male gender (Odds Ratio [OR] 3.23, Confidence Interval [CI] 95% 1.46-7.15), ICU admission (OR 2.78, CI 95% 1.29-5.96) and presence of SC at discharge (OR 14.39, CI 95% 6.41-32.32).
Conclusions: In our sample of patients with severe COVID-19, we found that PCC are highly variable and fluctuating over time; in particular, in about 50% of our patients new SC appear during follow up. Moreover, presence of PCC also in patients without SC at discharge and the variability of symptoms underlining the advisability of our multidisciplinary approach.
Trial registration number: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04424992, registered on 28 February 2020 https://www.
Clinicaltrials: gov/ct2/results?recrs=ab&cond=&term=NCT04424992&cntry=&state=&city=&dist The current version of protocol is version 1.0 enrolling since June 2020. The enrollment is still ongoing.
Keywords: COVID-19; ICU; Long-COVID; PASC; Post-COVID-19 conditions.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed H, Patel K, Greenwood DC, Halpin S, Lewthwaite P, Salawu A, Eyre L, Breen A, O'Connor R, Jones A, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes in survivors of severe acute respiratory syndrome and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus outbreaks after hospitalisation or ICU admission: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Rehabil Med. 2020;52(5):jrm00063. - PubMed
-
- Mandal S, Barnett J, Brill SE, Brown JS, Denneny EK, Hare SS, Heightman M, Hillman TE, Jacob J, Jarvis HC, et al. 'Long-COVID': a cross-sectional study of persisting symptoms, biomarker and imaging abnormalities following hospitalisation for COVID-19. Thorax. 2021;76(4):396–398. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-215818. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arnold DT, Hamilton FW, Milne A, Morley AJ, Viner J, Attwood M, Noel A, Gunning S, Hatrick J, Hamilton S, et al. Patient outcomes after hospitalisation with COVID-19 and implications for follow-up: results from a prospective UK cohort. Thorax. 2021;76(4):399–401. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-216086. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous