Nasal TSLP and periostin in infants with severe bronchiolitis and risk of asthma at 4 years of age
- PMID: 36694181
- PMCID: PMC9872300
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-023-02323-7
Nasal TSLP and periostin in infants with severe bronchiolitis and risk of asthma at 4 years of age
Abstract
Background: Severe bronchiolitis is often associated with subsequent respiratory morbidity, mainly recurrent wheezing and asthma. However, the underlying immune mechanisms remain unclear. The main goal of this study was to investigate the association of nasal detection of periostin and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) during severe bronchiolitis with the development of asthma at 4 years of age.
Methods: Observational, longitudinal, post-bronchiolitis, hospital-based, follow-up study. Children hospitalized for bronchiolitis between October/2013 and July/2017, currently aged 4 years, included in a previous study to investigate the nasal airway secretion of TSLP and periostin during bronchiolitis, were included. Parents were contacted by telephone, and were invited to a clinical interview based on a structured questionnaire to obtain information on the respiratory evolution. The ISAAC questionnaire for asthma symptoms for 6-7-year-old children, was also employed.
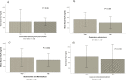
Results: A total of 248 children were included (median age 4.4 years). The mean age at admission for bronchiolitis was 3.1 (IQR: 1.5-6.5) months. Overall, 21% had ever been diagnosed with asthma and 37% had wheezed in the last 12 months. Measurable nasal TSLP was detected at admission in 27(11%) cases and periostin in 157(63%). The detection of nasal TSLP was associated with the subsequent prescription of maintenance asthma treatment (p = 0.04), montelukast (p = 0.01), and the combination montelukast/inhaled glucocorticosteroids (p = 0.03). Admissions for asthma tended to be more frequent in children with TSLP detection (p = 0.07). In the multivariate analysis, adjusting for potential confounders, the detection of TSLP remained independently associated with chronic asthma treatment prescription (aOR:2.724; CI 1.051-7.063, p:0.04) and with current asthma (aOR:3.41; CI 1.20-9.66, p:0.02). Nasal detection of periostin was associated with lower frequency of ever use of short-acting beta2-agonists (SABA) (p = 0.04), lower prevalence of current asthma (p = 0.02), less prescription of maintenance asthma treatment in the past 12 months (p = 0.02, respectively). In the multivariate analysis, periostin was associated with lower risk of asthma at 4 years, independently of the atopic status (aOR:0.511 CI 95% 0.284-0.918, p:0.025).
Conclusions: Our results show a positive correlation between nasal TSLP detection in severe bronchiolitis and the presence of current asthma, prescription of asthma maintenance treatment and respiratory admissions up to the age of 4 years. By contrast, we found a protective association between nasal periostin detection and current asthma at 4 years, ever diagnosis of asthma, maintenance asthma treatment prescription, and respiratory admissions.
Keywords: Asthma; Bronchiolitis; Periostin; Recurrent wheezing; Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV); Rhinovirus (HRV); Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, IL-33, and periostin in hospitalized infants with viral bronchiolitis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 May;96(18):e6787. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006787. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28471975 Free PMC article.
-
[Respiratory syncytial virus infection and asthma].Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2001 May-Jun;29(3):140-6. doi: 10.1016/s0301-0546(01)79034-9. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2001. PMID: 11434889 Review. Spanish.
-
Thymic stromal lymphopoietin is induced by respiratory syncytial virus-infected airway epithelial cells and promotes a type 2 response to infection.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Nov;130(5):1187-1196.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.031. Epub 2012 Sep 13. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22981788 Free PMC article.
-
Determinants of asthma after severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Jul;130(1):91-100.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.02.010. Epub 2012 Mar 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22444510 Free PMC article.
-
Rhinovirus-induced bronchiolitis and asthma development.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011 Jun;22(4):350-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2011.01170.x. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21535176 Review.
References
-
- Sigurs N, Bjarnason R, Sigurbergsson F, Kjellman B. Respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy is an important risk factor for asthma and allergy at age 7. Am J Respir Crit Care. 2000;161(5):1501–1507. - PubMed
-
- Sigurs N, Gustafsson PM, Bjarnason R, Lundberg F, Schmidt S, Sigurbergsson F, et al. Severe respiratory syncytial virus bronchiolitis in infancy and asthma and allergy at age 13. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;171(2):137–141. - PubMed
-
- Sigurs N, Aljassim F, Kjellman B, Robinson PD, Sigurbergsson F, Bjarnason R, et al. Asthma and allergy patterns over 18 years after severe RSV bronchiolitis in the first year of life. Thorax. 2010;65(12):1045–1052. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PI18/00044/FIS (Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria-Spanish Health Research Fund)
- PI15/00028/Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria-Spanish Health Research Fund
- VIII Convocatoria Santander-UAX/Fundación Universidad Alfonso X El Sabio
- Grant SENP 2018 (Beca Senior de Investigación)./Sociedad Española de Neumología Pediátrica
- Grant SEICAP: Convocatoria de Becas de Investigación SEICAP. Curso 2018-19./Sociedad Española de Inmunología Clínica y Alergia Pediátrica
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

