A trans-amplifying RNA simplified to essential elements is highly replicative and robustly immunogenic in mice
- PMID: 36694464
- PMCID: PMC10277886
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.01.019
A trans-amplifying RNA simplified to essential elements is highly replicative and robustly immunogenic in mice
Erratum in
-
A trans-amplifying RNA simplified to essential elements is highly replicative and robustly immunogenic in mice.Mol Ther. 2023 Jul 5;31(7):2297. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.06.001. Epub 2023 Jun 11. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37307814 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A trans-amplifying RNA simplified to essential elements is highly replicative and robustly immunogenic in mice.Mol Ther. 2024 Jan 3;32(1):257-259. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.11.024. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Mol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38043532 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
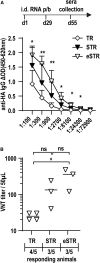
Trans-amplifying RNA (taRNA) is a split-vector derivative of self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) and a promising vaccine platform. taRNA combines a non-replicating mRNA encoding an alphaviral replicase and a transreplicon (TR) RNA coding for the antigen. Upon translation, the replicase amplifies the antigen-coding TR, thereby requiring minimal amounts of TR for immunization. TR amplification by the replicase follows a complex mechanism orchestrated by genomic and subgenomic promoters (SGPs) and generates genomic and subgenomic amplicons whereby only the latter are translated into therapeutic proteins. This complexity merits simplification to improve the platform. Here, we eliminated the SGP and redesigned the 5' untranslated region to shorten the TR (STR), thereby enabling translation of the remaining genomic amplicon. We then applied a directed evolution approach to select for faster replicating STRs. The resulting evolved STR (eSTR) had acquired A-rich 5' extensions, which improved taRNA expression thanks to accelerated replication. Consequently, we reduced the minimal required TR amount by more than 10-fold without losing taRNA expression in vitro. Accordingly, eSTR-immunized mice developed greater antibody titers to taRNA-encoded influenza HA than TR-immunized mice. In summary, this work points the way for further optimization of taRNA by combining rational design and directed evolution.
Keywords: alphaviral vector; directed evolution; trans-amplifying RNA; transreplicon; vaccine.
Copyright © 2023 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests U.S., T.B., and M.P. are inventors on patents and patent applications, which cover parts of this article. U.S. is employee at BioNTech Corporation (Mainz, Germany), a privately owned company developing therapeutic RNA.
Figures
Comment in
-
Trans-amplifying RNA: Translational application in gene therapy.Mol Ther. 2023 Jun 7;31(6):1507-1508. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.03.015. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Mol Ther. 2023. PMID: 37023758 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kumar A., Blum J., Thanh Le T., Havelange N., Magini D., Yoon I.-K. The mRNA vaccine development landscape for infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022;21:333–334. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

