Aging deteriorated liver Ischemia and reperfusion injury by suppressing Tribble's proteins 1 mediated macrophage polarization
- PMID: 36694470
- PMCID: PMC9995131
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2090218
Aging deteriorated liver Ischemia and reperfusion injury by suppressing Tribble's proteins 1 mediated macrophage polarization
Abstract
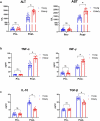
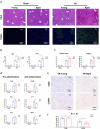
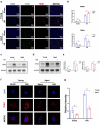
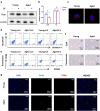
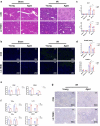
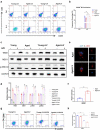
Aggravated liver injury has been reported in aged ischemia/reperfusion-stressed livers; however, the mechanism of aged macrophage inflammatory regulation is not well understood. Here, we found that the adaptor protein TRIB1 plays a critical role in the differentiation of macrophages and the inflammatory response in the liver after ischemia/reperfusion injury. In the present study, we determined that aging promoted macrophage-mediated liver injury and that inflammation was mainly responsible for lower M2 polarization in liver transplantation-exposed humans post I/R. Young and aged mice were subjected to hepatic I/R modeling and showed that aging aggravated liver injury and suppressed macrophage TRIB1 protein expression and anti-inflammatory function in I/R-stressed livers. Restoration of TRIB1 is mediated by lentiviral infection-induced macrophage anti-inflammatory M2 polarization and alleviated hepatic I/R injury. Moreover, TRIB1 overexpression in macrophages facilitates M2 polarization and anti-inflammation by activating MEK1-ERK1/2 signaling under IL-4 stimulation. Taken together, our results demonstrated that aging promoted hepatic I/R injury by suppressing TRIB1-mediated MEK1-induced macrophage M2 polarization and anti-inflammatory function.
Keywords: Liver ischemia/reperfusion injury; TRIB1; inflammation; macrophage; polarization.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Trib1 Contributes to Recovery From Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Regulating the Polarization of Renal Macrophages.Front Immunol. 2020 Mar 20;11:473. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00473. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32265926 Free PMC article.
-
Myeloid Deletion of Cdc42 Protects Liver From Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Inhibiting Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in Mice.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;17(6):965-981. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2024.01.023. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38342302 Free PMC article.
-
Tribbles homolog 1 deficiency modulates function and polarization of murine bone marrow-derived macrophages.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jul 20;293(29):11527-11536. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000703. Epub 2018 Jun 13. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29899113 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hepatic Macrophage Polarization and Apoptosis on Liver Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury During Liver Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 26;11:1193. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01193. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32676077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage Polarization and Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(5):1104-1113. doi: 10.7150/ijms.52691. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33526969 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jung KW, Kang J, Kwon H-M, et al. Effect of remote ischemic preconditioning conducted in living liver donors on postoperative liver function in donors and recipients following liver transplantation: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg. 2020;271(4):646–653. - PubMed
-
- Kan C, Ungelenk L, Lupp A, et al. Ischemia-reperfusion injury in aged livers-the energy metabolism, inflammatory response, and autophagy. Transplantation. 2018;102(3):368–377. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
