Comparison of the Effect of Injectable Tranexamic Acid and Inhaled Desmopressin in Controlling Bleeding and Ecchymosis in Open Rhinoplasty
- PMID: 36694687
- PMCID: PMC9840754
- DOI: 10.52547/wjps.11.3.24
Comparison of the Effect of Injectable Tranexamic Acid and Inhaled Desmopressin in Controlling Bleeding and Ecchymosis in Open Rhinoplasty
Abstract
Background: Bleeding during rhinoplasty surgery has a negative effect on the quality of surgery; so, it is important to reduce bleeding during rhinoplasty. We aimed to evaluate the effect of injectable tranexamic acid (TXA) and nasal spray of desmopressin (DDAVP) on reduction in intraoperative bleeding and ecchymosis after open rhinoplasty.
Methods: In a Randomized Clinical Trial ( RCT) prepared since 2020 to 2021 in Razi Hospital and Imam Khomeini Hospital, Tehran, Iran on 42 patients who underwent open rhinoplasty were divided into three groups. In the first group, TXA was injected one hour before surgery at a dose of 10 mg / kg with a placebo inhalation spray. In the second group, DDAVP was administered as a nasal spray at a dose of 40 mcg with a placebo injection. The third group received a placebo spray and placebo injection. All required data were gathered and analyzed.
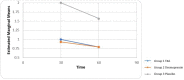
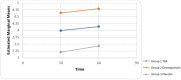
Results: In TXA group and DDAVP groups, the volume of bleeding during surgery significantly (P=0.022) decreased compared to placebo group, also, the quality of the surgical field and the surgeon's satisfaction significantly (P=0.007) improved compared to the placebo group but not with each other. Unlike placebo group, there were no reports of postoperative bleeding in the TXA and DDAVP groups. Duration of surgery, ecchymosis on the day after surgery and coagulation tests before and after surgery were not significantly different in three groups.
Conclusion: Use of DDAVP and TXA can both reduce the amount of bleeding during surgery and postoperative bleeding in rhinoplasty and improve the quality of the surgical field and the surgeon 's satisfaction during surgery.
Keywords: Ecchymosis; Inhaled Desmopressin; Rhinoplasty; Tranexamic Acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Erişir F, Tahamiler R. Lateral osteotomies in rhinoplasty: a safer and less traumatic method. Aesthet Surg J. 2008 Sep-Oct;28(5):518–20. - PubMed
-
- Cochran CS, Landecker A. Prevention and management of rhinoplasty complications. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008 Aug;122(2):60e–67e. - PubMed
-
- Ozkose M, Baykan H, Coşkuner İ. The Effect of Patient Positioning on Amount of Intraoperative Bleeding in Rhinoplasty: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2016 Aug;40(4):453–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources