Assessment the Effect of Human Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly Stem Cells on the Expression of Homing Genes: CXCR4 and VLA-4 in Cell Line of Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 36694702
- PMCID: PMC9831870
- DOI: 10.18502/ijhoscr.v16i3.10138
Assessment the Effect of Human Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly Stem Cells on the Expression of Homing Genes: CXCR4 and VLA-4 in Cell Line of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
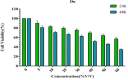
Background : Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in the male that affects the health, social and economic life of person. Different compounds such as Wharton's jelly, have been used to treat prostate cancer. Wharton's jelly is a tissue rich in cells with mesenchymal morphology. Wharton's jelly compound inhibited the growth of various cancer cells, including ovarian, osteosarcoma, breast, and prostate cancers, and also reduced the expression of CXCR4 and VLA-4 genes involved in the metastasis process. Materials and Methods: To do this research, Wharton's jelly stem cells and DU145 cancer cell line were cultured. After cell culture, the effect of Wharton's jelly on this cell line was evaluated by scratching and MTT assay. The expression of CXCR4 and VLA-4 genes was also evaluated by Real-time PCR. Results: The results of MTT and Scratching tests showed that Wharton's jelly inhibited the growth of DU145 cancer cells and also decreased the expression level of CXCR4 and VLA-4 genes. Conclusion: The results of this study showed that Wharton's jelly can be considered as an effective compound for decreasing metastasis of prostate cancer.
Keywords: CXCR4 gene; Prostate cancer; VLA-4 gene; Wharton jelly.
Copyright © 2022 Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Assessment the Effect of Human Umbilical Cord Wharton's Jelly Stem Cells on the Expression of Homing Genes; CXCR4 and VLA-4 in Cell Line of Breast Cancer.Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2022 Apr 1;16(2):110-116. doi: 10.18502/ijhoscr.v16i2.9204. Int J Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 2022. PMID: 36304731 Free PMC article.
-
Human umbilical cord Wharton's Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiation into nerve-like cells.Chin Med J (Engl). 2005 Dec 5;118(23):1987-93. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005. PMID: 16336835
-
Umbilical cord-derived Wharton's jelly for regenerative medicine applications in orthopedic surgery: a systematic review protocol.J Orthop Surg Res. 2020 Nov 11;15(1):527. doi: 10.1186/s13018-020-02067-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020. PMID: 33176838 Free PMC article.
-
Wharton's Jelly stem cells: future clinical applications.Placenta. 2011 Oct;32 Suppl 4:S311-5. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2011.06.010. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Placenta. 2011. PMID: 21733573 Review.
-
Absence of Wharton's Jelly at the Abdominal Site of the Umbilical Cord Insertion. Rare Case Report and Review of the Literature.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Nov 18;57(11):1268. doi: 10.3390/medicina57111268. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34833486 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jemal A, Murray t, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55(1):10. - PubMed
-
- Carter H, Partin A, Retik A, et al. Diagnosis and staging of prostate cancer Campbell, s urology. Sydney: Elsevier science publishers; 2002.
-
- Chambers AF, Groom AC, MacDonald IC. Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat Rev Cancer . 2002;2(8):563–72. - PubMed
-
- Available from: https://www.britannica.com/science/metastasis.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
