Changes in serum lipids with the onset and progression of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type-II Diabetes Mellitus
- PMID: 36694747
- PMCID: PMC9842978
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.39.1.6265
Changes in serum lipids with the onset and progression of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type-II Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the role of serum lipids in the onset and progression of Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) in Type-II diabetes (T2DM) individuals.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted at the National Institute of Diabetes and Endocrinology (NIDE), Dow University of Health Sciences (DUHS) from March to May 2019. After signing the informed consent, healthy controls (n=30), T2DM patients (diabetic n=30), proliferative (PDR n=30) and non-proliferative (NPDR n= 30) of age 18 to 65 years were selected by convenient sampling. Background information was gathered through interviews and the fundoscopy was done. Fasting five ml venous blood samples were collected and analysed for triglycerides (TGs), cholesterol, HDL, LDL, VLDL and the HbA1c using commercially available assays. The SPSS, version 24.0, was used for data analysis.
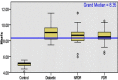
Results: The HbA1c level was high in the diabetes, NPDR and PDR groups than control (p<0.05). The serum TGs and cholesterol were raised while the HDL was low in the diabetes group than in control (p<0.05). The cholesterol and LDL were high in the diabetes group compared to NPDR and PDR groups (p<0.05). The cholesterol and VLDL showed a positive moderately strong correlation with HbA1c in the PDR group (p<0.05).
Conclusion: The serum lipid levels vary with the HbA1c levels and greater degree of derangement is observed with increasing mean HbA1C independent of diabetic retinopathy. For this reason, strict control of HbA1c and serum lipid level by lifestyle and/or pharmacologic intervention is recommended in diabetes with or without retinopathy.
Keywords: Diabetic Retinopathy; Dyslipidemia; Type-II Diabetes Mellitus.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Dyslipidemia with Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Hospital-Based Study.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021 Nov;13(Suppl 2):S1062-S1067. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_164_21. Epub 2021 Nov 10. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2021. PMID: 35017930 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic factors for the development and progression of proliferative diabetic retinopathy in people with diabetic retinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 22;2(2):CD013775. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013775.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36815723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma Apolipoproteins Predicting the Occurrence and Severity of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;13:915575. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.915575. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35937834 Free PMC article.
-
Association of serum lipid levels with diabetic retinopathy.Int J Ophthalmol. 2013 Jun 18;6(3):346-9. doi: 10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.03.17. Print 2013. Int J Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 23826531 Free PMC article.
-
Creatinine as a predictor of proliferative diabetic retinopathy among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2025 Jun 3. doi: 10.1007/s11255-025-04590-3. Online ahead of print. Int Urol Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40461778 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation analysis of Type-2 diabetes mellitus with proliferative retinopathy and central macular thickness.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Mar-Apr;40(4):642-647. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.4.7726. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38545017 Free PMC article.
-
Dates fruit effects on dyslipidemia among patients with Type-2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials.Pak J Med Sci. 2025 Jan;41(1):331-337. doi: 10.12669/pjms.41.1.9928. Pak J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 39867809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive value of triglyceride glucose index and systemic inflammation index for diabetic retinopathy in Type-2 diabetes.Pak J Med Sci. 2025 Apr;41(4):1072-1077. doi: 10.12669/pjms.41.4.11374. Pak J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40290244 Free PMC article.
-
The Predictors of Early Treatment Effectiveness of Intravitreal Bevacizumab Application in Patients with Diabetic Macular Edema.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 May 10;14(10):992. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14100992. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38786290 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated waist-to-hip ratio, as an abdominal obesity index, predicts the risk of diabetic kidney injury.World J Diabetes. 2025 Apr 15;16(4):101384. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i4.101384. World J Diabetes. 2025. PMID: 40236864 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shanthi T, Sabeenian RS. Modified Alexnet architecture for classification of diabetic retinopathy images. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019;76:56–64. doi:10.1016/j.compeleceng.2019.03.004.
-
- Pandova MG. Diabetic retinopathy and blindness:An epidemiological overview. Visual Impairment and Blindness-What We Know and What We Have to Know. 2019 Aug 19; doi:10.5772/intechopen.8∴.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources