Placenta increta in an unscarred and bicornute uterus
- PMID: 36694782
- PMCID: PMC9842992
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.39.1.6164
Placenta increta in an unscarred and bicornute uterus
Abstract
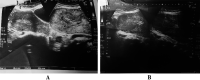
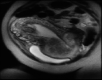
Morbidly adherent placenta is a spectrum of obstetric complication which is life threatening to both mother and fetus. Congenital uterine malformation is a rare cause of such a condition. Here we present a case report of placenta increta in bicornute, unscarred uterus. An 18 year old para1+1 presented in emergency with history of vaginal delivery of still birth baby followed by vaginal bleeding with retained placenta. Her Examination under anaesthesia and failed attempt of manual removal of the placenta performed in emergency followed by Doppler ultrasound showed a bicornuate uterus with possibility of placenta increta, later this diagnosis was confirmed on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Patient managed with injection methotrexate along with folinic acid followed by removal of placenta under general anesthesia, hence we preserved her fertility. The aim of this report is to emphasize the importance of this rare but a possible association of nonscar and malformed uterus with spectrum of abnormal placentation. Obstetrician should run a full set of investigations in such cases to prevent maternal and fetal mortality and morbidity.
Keywords: Bicornute uterus; Placenta Increta; Unscarred uterus.
Copyright: © Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures
References
-
- Fleisch M C, Lux J, Schoppe M, Grieshaber K, Hampl M. Placenta Percreta Leading to Spontaneous Complete Uterine Rupture in the Second Trimester. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 2008;65:81–83. doi:10.1159/000108288. - PubMed
-
- Anderson S, Lekovic J, Niemasik E, Chasen ST. Patients with uterine anamolies may have a risk of placenta accrete. Fertil Steril. 2013;100(3):S379–801. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.07.744.
-
- Meriem NADI. Placenta accreta:Case report presenting obstetric emergency Gynecology &Obstetrics Case report 2020. World Congr Gynecol Obstet. 2020;6(5):2471–8165.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources