Trends in incidence rates of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective study in Isfahan province, Iran
- PMID: 36695001
- PMCID: PMC9951581
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13975
Trends in incidence rates of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective study in Isfahan province, Iran
Abstract
Aims/introduction: We aimed to determine the incidence trend of childhood type 1 diabetes mellitus in Isfahan province over a period of 12 years.
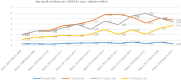
Materials and methods: In this retrospective study, children aged <20 years at the time of type 1 diabetes mellitus diagnosis, from March 2007 to March 2019, were included. The crude and adjusted incidence rate of type 1 diabetes mellitus is calculated as the number of cases per 100,000 person-years by the period. The cumulative, age- and sex-specific incidence rates were also calculated. Age-specific incidence rates were calculated for age and sex groups.
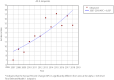
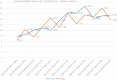
Results: A total of 1,954 (983 boys and 971 girls) cases of type 1 diabetes mellitus were identified. The mean age at diagnosis in all studied populations was 9.89 (standard deviation 4.76). There were no significant differences between the proportion of boys and girls in different years (P = 0.12) and different age groups (P = 0.19). The average annual percent change of incidence rate for the total population, for girls and boys, was 6.9%, 6.7% and 6.3% respectively. The type 1 diabetes mellitus incidence rate had a significant trend to be increased from 2007 to 2019 (P < 0.001, t = 3.6).
Conclusion: Our findings showed that currently our region is considered a region with a high incidence rate of type 1 diabetes mellitus. Although we have had fluctuations in the incidence rate over the 12 years, the overall trend is increasing.
Keywords: Incidence; Trend; Type 1 diabetes mellitus.
© 2023 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increasing Trends of Pediatric Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures in the United States from 2004 to 2023: A 20-year National Injury Review Depicting Shifts in Mechanisms of Injury.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Feb 25;483(8):1542-1553. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003421. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40036050
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of periodontal disease for glycaemic control in people with diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 6;2015(11):CD004714. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004714.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 14;4:CD004714. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004714.pub4. PMID: 26545069 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Intensive glucose control versus conventional glucose control for type 1 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Feb 14;2014(2):CD009122. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009122.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. PMID: 24526393 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Comparative Study on the Effectiveness of Unified Protocols for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders and Modular Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy on Positive and Negative Affect, and Emotional Awareness in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus.Adv Biomed Res. 2025 Jan 30;14:4. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_239_24. eCollection 2025. Adv Biomed Res. 2025. PMID: 40213593 Free PMC article.
-
The increase in diabetes in children from underdeveloped countries.Curr Opin Pediatr. 2024 Aug 1;36(4):467-472. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000001366. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38832684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes in Podlasie region, Poland, in years 2010-2022 - 13-years-single-center study, including COVID-19 pandemic perspective.Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2025;31(1):9-16. doi: 10.5114/pedm.2025.149201. Pediatr Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40353383 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lucier J, Weinstock RS. Diabetes mellitus type 1. In: StatPearls (ed). Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing, 2021.
-
- Sussman M, Benner J, Haller MJ, et al. Estimated lifetime economic burden of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2020; 22: 121–130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

