Analysis of regulatory sequences in exosomal DNA of NANOGP8
- PMID: 36696426
- PMCID: PMC9876286
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280959
Analysis of regulatory sequences in exosomal DNA of NANOGP8
Abstract
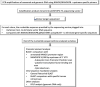
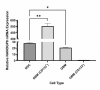
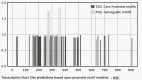
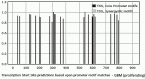
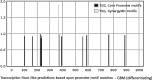
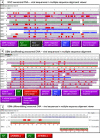
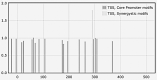
Exosomes participate in intercellular communication by transporting functionally active molecules. Such cargo from the original cells comprising proteins, micro-RNA, mRNA, single-stranded (ssDNA) and double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) molecules pleiotropically transforms the target cells. Although cancer cells secrete exosomes carrying a significant level of DNA capable of modulating oncogene expression in a recipient cell, the regulatory mechanism is unknown. We have previously reported that cancer cells produce exosomes containing NANOGP8 DNA. NANOGP8 is an oncogenic paralog of embryonic stem cell transcription factor NANOG and does not express in cells since it is a pseudogene. However, in this study, we evaluated NANOGP8 expression in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) tissue from a surgically removed brain tumor of a patient. Significantly higher NANOGP8 transcription was observed in GBM cancer stem cells (CSCs) than in GBM cancer cells or neural stem cells (NSCs), despite identical sequences of NANOGP8-upstream genomic region in all the cell lines. This finding suggests that upstream genomic sequences of NANOGP8 may have environment-dependent promoter activity. We also found that the regulatory sequences upstream of exosomal NANOGP8 GBM DNA contain multiple core promoter elements, transcription factor binding sites, and segments of human viruses known for their oncogenic role. The exosomal sequence of NANOGP8-upstream GBM DNA is different from corresponding genomic sequences in CSCs, cancer cells, and NSCs as well as from the sequences reported by NCBI. These sequence dissimilarities suggest that exosomal NANOGP8 GBM DNA may not be a part of the genomic DNA. Exosomes possibly acquire this DNA from other sources where it is synthesized by an unknown mechanism. The significance of exosome-bestowed regulatory elements in the transcription of promoter-less retrogene such as NANOGP8 remains to be determined.
Copyright: © 2023 Vaidya et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Differential sequences of exosomal NANOG DNA as a potential diagnostic cancer marker.PLoS One. 2018 May 22;13(5):e0197782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197782. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29787607 Free PMC article.
-
Differential sequences and single nucleotide polymorphism of exosomal SOX2 DNA in cancer.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 24;15(2):e0229309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229309. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32092088 Free PMC article.
-
Fli-1 promotes proliferation and upregulates NANOGP8 expression in T-lymphocyte leukemia cells.Biochimie. 2020 Jan;168:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2019.10.005. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Biochimie. 2020. PMID: 31626853
-
Exosomal noncoding RNAs: key players in glioblastoma drug resistance.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Nov;476(11):4081-4092. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04221-2. Epub 2021 Jul 17. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34273059 Review.
-
MiR-21: A key player in glioblastoma pathogenesis.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Feb;119(2):1285-1290. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26300. Epub 2017 Aug 28. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 28727188 Review.
Cited by
-
NAT10-mediated ac4C modification promotes stemness and chemoresistance of colon cancer by stabilizing NANOGP8.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 25;10(9):e30330. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30330. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38726177 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle-associated DNA: ten years since its discovery in human blood.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Sep 12;15(9):668. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07003-y. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39266560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Based Characterization of Stem Cell Phenotype in Glioblastomas.Cureus. 2024 Sep 28;16(9):e70403. doi: 10.7759/cureus.70403. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39473666 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-mediated macrophage regulation for inflammatory bowel disease repair: a potential target of gut inflammation.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Dec 15;15(12):6970-6987. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38186999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomes Induce Crosstalk Between Multiple Types of Cells and Cardiac Fibroblasts: Therapeutic Potential for Remodeling After Myocardial Infarction.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Oct 19;19:10605-10621. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S476995. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39445157 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burster T, Traut R, Yermekkyzy Z, Mayer K, Westhoff M-A, Bischof J, et al. Critical View of Novel Treatment Strategies for Glioblastoma: Failure and Success of Resistance Mechanisms by Glioblastoma Cells. Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 2021:2290. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.695325 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

