Targeted next-generation sequencing has incremental value in the diagnostic work-up of patients with suspect pancreatic masses; a multi-center prospective cross sectional study
- PMID: 36696439
- PMCID: PMC9876380
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280939
Targeted next-generation sequencing has incremental value in the diagnostic work-up of patients with suspect pancreatic masses; a multi-center prospective cross sectional study
Abstract
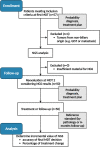
Background: The diagnostic process of patients with suspect pancreatic lesions is often lengthy and prone to repeated diagnostic procedures due to inconclusive results. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) performed on cytological material obtained with fine needle aspiration (FNA) or biliary duct brushing can speed up this process. Here, we study the incremental value of NGS for establishing the correct diagnosis, and subsequent treatment plan in patients with inconclusive diagnosis after regular diagnostic work-up for suspect pancreatic lesions.
Methods: In this prospective cross-sectional cohort study, patients were screened for inclusion in four hospitals. NGS was performed with AmpliSeq Cancer Hotspot Panel v2 and v4b in patients with inconclusive cytology results or with an uncertain diagnosis. Diagnostic results were evaluated by the oncology pancreatic multidisciplinary team. The added value of NGS was determined by comparing diagnosis (malignancy, cystic lesion or benign condition) and proposed treatment plan (exploration/resection, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, follow-up, palliation or repeated FNA) before and after integration of NGS results. Final histopathological analysis or a 6-month follow-up period were used as the reference standard in case of surgical intervention or non-invasive treatment, respectively.
Results: In 50 of the 53 included patients, cytology material was sufficient for NGS analysis. Diagnosis before and after integration of NGS results differed in 24% of the patients. The treatment plan was changed in 32% and the diagnosis was substantiated by the NGS data in 44%. Repetition of FNA/brushing was prevented in 14% of patients. All changes in treatment plan were correctly made after integration of NGS. Integration of NGS increased overall diagnostic accuracy from 68% to 94%.
Interpretation: This study demonstrates the incremental diagnostic value of NGS in patients with an initial inconclusive diagnosis. Integration of NGS results can prevent repeated EUS/FNA, and can also rigorously change the final diagnosis and treatment plan.
Copyright: © 2023 Achterberg et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gerritsen A, Molenaar IQ, Bollen TL, Nio CY, Dijkgraaf MG, van Santvoort HC, et al.. Preoperative characteristics of patients with presumed pancreatic cancer but ultimately benign disease: a multicenter series of 344 pancreatoduodenectomies. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(12):3999–4006. doi: 10.1245/s10434-014-3810-7 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sibinga Mulder B. Diagnostic Value of Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing in Patients with Suspected Pancreatic of Periampullary Cancer. 2017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical