Ufmylation reconciles salt stress-induced unfolded protein responses via ER-phagy in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 36696447
- PMCID: PMC9945950
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2208351120
Ufmylation reconciles salt stress-induced unfolded protein responses via ER-phagy in Arabidopsis
Abstract
In plants, the endomembrane system is tightly regulated in response to environmental stresses for maintaining cellular homeostasis. Autophagosomes, the double membrane organelles forming upon nutrient deprivation or stress induction, degrade bulky cytosolic materials for nutrient turnover. Though abiotic stresses have been reported to induce plant autophagy, few receptors or regulators for selective autophagy have been characterized for specific stresses. Here, we have applied immunoprecipitation followed by tandem mass spectrometry using the autophagosome marker protein ATG8 as bait and have identified the E3 ligase of the ufmylation system Ufl1 as a bona fide ATG8 interactor under salt stress. Notably, core components in the ufmylation cascade, Ufl1 and Ufm1, interact with the autophagy kinase complexes proteins ATG1 and ATG6. Cellular and genetic analysis showed that Ufl1 is important for endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-phagy under persisting salt stress. Loss-of-function mutants of Ufl1 display a salt stress hypersensitive phenotype and abnormal ER morphology. Prolonged ER stress responses are detected in ufl1 mutants that phenocopy the autophagy dysfunction atg5 mutants. Consistently, expression of ufmylation cascade components is up-regulated by salt stress. Taken together, our study demonstrates the role of ufmylation in regulating ER homeostasis under salt stress through ER-phagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
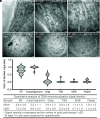
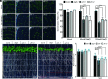
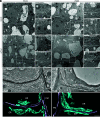
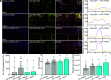

Similar articles
-
Ufmylation bridges autophagy and ER homeostasis in plants.Autophagy. 2023 Oct;19(10):2830-2831. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2203985. Epub 2023 May 1. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 37126567 Free PMC article.
-
A cross-kingdom conserved ER-phagy receptor maintains endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis during stress.Elife. 2020 Aug 27;9:e58396. doi: 10.7554/eLife.58396. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32851973 Free PMC article.
-
C53 is a cross-kingdom conserved reticulophagy receptor that bridges the gap betweenselective autophagy and ribosome stalling at the endoplasmic reticulum.Autophagy. 2021 Feb;17(2):586-587. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1846304. Epub 2020 Dec 3. Autophagy. 2021. PMID: 33164651 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of ER stress-mediated autophagy and ER-phagy: Involvement of UPR and the core autophagy machinery.J Cell Physiol. 2018 May;233(5):3867-3874. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26137. Epub 2017 Aug 30. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 28777470 Review.
-
Ufl1/RCAD, a Ufm1 E3 ligase, has an intricate connection with ER stress.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Aug 15;135:760-767. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.170. Epub 2019 May 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31129212 Review.
Cited by
-
Charting the evolutionary path of the SUMO modification system in plants reveals molecular hardwiring of development to stress adaptation.Plant Cell. 2024 Sep 3;36(9):3131-3144. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koae192. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38923935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stress granules sequester autophagy proteins to facilitate plant recovery from heat stress.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 30;15(1):10910. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55292-w. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39738069 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Rhizobia Endosymbiosis by Coupling ER Expansion with Enhanced UPR.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025 Apr;12(15):e2414519. doi: 10.1002/advs.202414519. Epub 2025 Feb 22. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2025. PMID: 39985282 Free PMC article.
-
Ufmylation bridges autophagy and ER homeostasis in plants.Autophagy. 2023 Oct;19(10):2830-2831. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2203985. Epub 2023 May 1. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 37126567 Free PMC article.
-
The UFMylation pathway is impaired in Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurodegener. 2024 Dec 18;19(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00784-y. Mol Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39696466 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Millar A. H., et al. , The scope, functions, and dynamics of posttranslational protein modifications. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 70, 119–151 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Komander D., Rape M., The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 81, 203–229 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Pickart C. M., Eddins M. J., Ubiquitin: Structures, functions, mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1695, 55–72 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Popovic D., Vucic D., Dikic I., Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Med. 20, 1242–1253 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

