Development of mRNA Vaccines/Therapeutics and Their Delivery System
- PMID: 36697236
- PMCID: PMC9880606
- DOI: 10.14348/molcells.2023.2165
Development of mRNA Vaccines/Therapeutics and Their Delivery System
Abstract
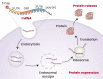
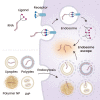
The rapid development of mRNA vaccines has contributed to the management of the current coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, suggesting that this technology may be used to manage future outbreaks of infectious diseases. Because the antigens targeted by mRNA vaccines can be easily altered by simply changing the sequence present in the coding region of mRNA structures, it is more appropriate to develop vaccines, especially during rapidly developing outbreaks of infectious diseases. In addition to allowing rapid development, mRNA vaccines have great potential in inducing successful antigen-specific immunity by expressing target antigens in cells and simultaneously triggering immune responses. Indeed, the two COVID-19 mRNA vaccines approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration have shown significant efficacy in preventing infections. The ability of mRNAs to produce target proteins that are defective in specific diseases has enabled the development of options to treat intractable diseases. Clinical applications of mRNA vaccines/therapeutics require strategies to safely deliver the RNA molecules into targeted cells. The present review summarizes current knowledge about mRNA vaccines/ therapeutics, their clinical applications, and their delivery strategies.
Keywords: RNA delivery; RNA therapeutics; mRNA therapeutics; mRNA vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

