Utilisation of exome sequencing for muscular disorders in Thai paediatric patients: diagnostic yield and mutational spectrum
- PMID: 36697461
- PMCID: PMC9876991
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-28405-6
Utilisation of exome sequencing for muscular disorders in Thai paediatric patients: diagnostic yield and mutational spectrum
Abstract
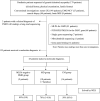
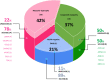
Muscular dystrophies and congenital myopathies are heterogeneous groups of inherited muscular disorders. An accurate diagnosis is challenging due to their complex clinical presentations and genetic heterogeneity. This study aimed to determine the utilisation of exome sequencing (ES) for Thai paediatric patients with muscular disorders. Of 176 paediatric patients suspected of genetic/inherited myopathies, 133 patients received a molecular diagnosis after performing conventional investigations, single gene testing, and gene panels. The remaining 43 patients from 42 families could be classified into three groups: Group 1, MLPA-negative Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) with 9 patients (9/43; 21%), Group 2, other muscular dystrophies (MD) with 18 patients (18/43; 42%) and Group 3, congenital myopathies (CM) with 16 patients (16/43; 37%). All underwent exome sequencing which could identify pathogenic variants in 8/9 (89%), 14/18 (78%), and 8/16 (50%), for each Group, respectively. Overall, the diagnostic yield of ES was 70% (30/43) and 36 pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants in 14 genes were identified. 18 variants have never been previously reported. Molecular diagnoses provided by ES changed management in 22/30 (73%) of the patients. Our study demonstrates the clinical utility and implications of ES in inherited myopathies.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical