Use of thoracoscopy for thoracic sympathetic nerve block in primary hyperhidrosis
- PMID: 36697462
- PMCID: PMC9876953
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-28727-5
Use of thoracoscopy for thoracic sympathetic nerve block in primary hyperhidrosis
Abstract
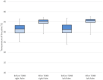
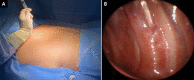
Thoracic sympathetic nerve block (TSNB) has been widely used in the treatment of neuropathic pain. To reduce block failure rates, TSNB is assisted with several modalities including fluoroscopy, computed tomography, and ultrasonography. The present study describes our experience assessing the usefulness of thoracoscopy in TSNB for predicting compensatory hyperhidrosis before sympathectomy in primary hyperhidrosis. From September 2013 to October 2021, TSNB was performed under local anesthesia using a 2-mm thoracoscope in 302 patients with severe primary hyperhidrosis. Among the 302 patients, 294 were included for analysis. The target level of TSNB was T3 in almost all patients. The mean procedure time was 21 min. Following TSNB, the mean temperature of the left and right palms significantly changed from 31.5 to 35.3 °C and from 31.5 to 34.8 °C, respectively. With TSNB, primary hyperhidrosis was relieved in all patients. Pneumothorax occurred in six patients, in which no chest tube insertion was required. One patient developed hemothorax and was discharged the next day after small-bore catheter drainage. Transient ptosis developed in 10 patients and improved within a day in all patients. Our experiences showed that thoracoscopic TSNB is accurate, safe, and feasible to block the thoracic sympathetic nerve in patients with severe primary hyperhidrosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

