Evaluation of 3'-phosphate as a transient protecting group for controlled enzymatic synthesis of DNA and XNA oligonucleotides
- PMID: 36697944
- PMCID: PMC9814670
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-022-00685-5
Evaluation of 3'-phosphate as a transient protecting group for controlled enzymatic synthesis of DNA and XNA oligonucleotides
Abstract
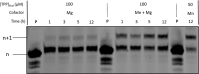
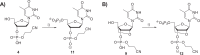
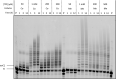
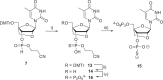
Chemically modified oligonucleotides have advanced as important therapeutic tools as reflected by the recent advent of mRNA vaccines and the FDA-approval of various siRNA and antisense oligonucleotides. These sequences are typically accessed by solid-phase synthesis which despite numerous advantages is restricted to short sequences and displays a limited tolerance to functional groups. Controlled enzymatic synthesis is an emerging alternative synthetic methodology that circumvents the limitations of traditional solid-phase synthesis. So far, most approaches strived to improve controlled enzymatic synthesis of canonical DNA and no potential routes to access xenonucleic acids (XNAs) have been reported. In this context, we have investigated the possibility of using phosphate as a transient protecting group for controlled enzymatic synthesis of DNA and locked nucleic acid (LNA) oligonucleotides. Phosphate is ubiquitously employed in natural systems and we demonstrate that this group displays most characteristics required for controlled enzymatic synthesis. We have devised robust synthetic pathways leading to these challenging compounds and we have discovered a hitherto unknown phosphatase activity of various DNA polymerases. These findings open up directions for the design of protected DNA and XNA nucleoside triphosphates for controlled enzymatic synthesis of chemically modified nucleic acids.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Towards the controlled enzymatic synthesis of LNA containing oligonucleotides.Front Chem. 2023 Apr 27;11:1161462. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1161462. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 37179777 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic Synthesis of 7',5'-Bicyclo-DNA Oligonucleotides.Chem Asian J. 2017 Jun 19;12(12):1347-1352. doi: 10.1002/asia.201700374. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Chem Asian J. 2017. PMID: 28371464
-
Controlled enzymatic synthesis of oligonucleotides.Commun Chem. 2024 Jun 18;7(1):138. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01216-0. Commun Chem. 2024. PMID: 38890393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Polymerase Variants with High Processivity and Accuracy for Encoding and Decoding Locked Nucleic Acid Sequences.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Dec 23;142(51):21530-21537. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c10902. Epub 2020 Dec 11. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 33306372
-
Nucleic acid joining enzymes: biological functions and synthetic applications beyond DNA.Biochem J. 2025 Jan 22;482(2):39-56. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20240136. Biochem J. 2025. PMID: 39840831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evolving a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase for commercial enzymatic DNA synthesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Feb 8;53(4):gkaf115. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf115. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 39988321 Free PMC article.
-
Template-dependent DNA ligation for the synthesis of modified oligonucleotides.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 13;15(1):8009. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52141-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39271668 Free PMC article.
-
A toolbox for enzymatic modification of nucleic acids with photosensitizers for photodynamic therapy.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 Jul 8;5(9):841-852. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00103f. eCollection 2024 Aug 28. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39211468 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphates as Assisting Groups in Glycan Synthesis.ACS Cent Sci. 2023 Dec 20;10(1):138-142. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.3c00896. eCollection 2024 Jan 24. ACS Cent Sci. 2023. PMID: 38292611 Free PMC article.
-
The XNA alphabet.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf635. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf635. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40650979 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

