Effect of Contrast Level and Image Format on a Deep Learning Algorithm for the Detection of Pneumothorax with Chest Radiography
- PMID: 36698035
- PMCID: PMC10287877
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-022-00772-y
Effect of Contrast Level and Image Format on a Deep Learning Algorithm for the Detection of Pneumothorax with Chest Radiography
Abstract
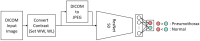
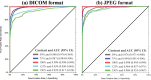
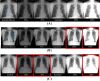
Under the black-box nature in the deep learning model, it is uncertain how the change in contrast level and format affects the performance. We aimed to investigate the effect of contrast level and image format on the effectiveness of deep learning for diagnosing pneumothorax on chest radiographs. We collected 3316 images (1016 pneumothorax and 2300 normal images), and all images were set to the standard contrast level (100%) and stored in the Digital Imaging and Communication in Medicine and Joint Photographic Experts Group (JPEG) formats. Data were randomly separated into 80% of training and 20% of test sets, and the contrast of images in the test set was changed to 5 levels (50%, 75%, 100%, 125%, and 150%). We trained the model to detect pneumothorax using ResNet-50 with 100% level images and tested with 5-level images in the two formats. While comparing the overall performance between each contrast level in the two formats, the area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC) was significantly different (all p < 0.001) except between 125 and 150% in JPEG format (p = 0.382). When comparing the two formats at same contrast levels, AUC was significantly different (all p < 0.001) except 50% and 100% (p = 0.079 and p = 0.082, respectively). The contrast level and format of medical images could influence the performance of the deep learning model. It is required to train with various contrast levels and formats of image, and further image processing for improvement and maintenance of the performance.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Contrast level; Deep learning; Image format; Pneumothorax.
© 2023. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automated detection of moderate and large pneumothorax on frontal chest X-rays using deep convolutional neural networks: A retrospective study.PLoS Med. 2018 Nov 20;15(11):e1002697. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002697. eCollection 2018 Nov. PLoS Med. 2018. PMID: 30457991 Free PMC article.
-
Do comprehensive deep learning algorithms suffer from hidden stratification? A retrospective study on pneumothorax detection in chest radiography.BMJ Open. 2021 Dec 7;11(12):e053024. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-053024. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34876430 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of digital radiography for the detection of pneumothorax: comparison with conventional chest radiography.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992 Mar;158(3):509-14. doi: 10.2214/ajr.158.3.1738985. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992. PMID: 1738985
-
Deep learning-based detection system for multiclass lesions on chest radiographs: comparison with observer readings.Eur Radiol. 2020 Mar;30(3):1359-1368. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06532-x. Epub 2019 Nov 20. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31748854
-
Deep Learning for Pneumothorax Detection on Chest Radiograph: A Diagnostic Test Accuracy Systematic Review and Meta Analysis.Can Assoc Radiol J. 2024 Aug;75(3):525-533. doi: 10.1177/08465371231220885. Epub 2024 Jan 8. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2024. PMID: 38189265
References
-
- Hwang EJ, Park S, Jin KN, Kim JI, Choi SY, Lee JH, et al: Deep Learning-Based Automatic Detection Algorithm Development and Evaluation Group. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning-based Automatic Detection Algorithm for Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis on Chest Radiographs. Clin Infect Dis 69(5):739–747, 2019 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

