The Virtual Radiology Reading Room: Initial Perceptions of Referring Providers and Radiologists
- PMID: 36698036
- PMCID: PMC9876648
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-022-00745-1
The Virtual Radiology Reading Room: Initial Perceptions of Referring Providers and Radiologists
Abstract
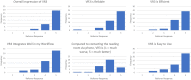
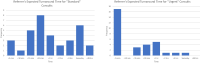
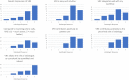
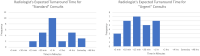
The objective of this study is to assess the initial perception of referring providers and radiologists to a virtual consultation solution (the Virtual Radiology Reading Room, VR3). VR3 is specifically designed to replace the radiology reading room phone and enable the radiologist to continue to work as part of the clinical care team fielding radiology consults without being confined to the same physical space. Surveys of providers' and radiologists' initial experience were conducted approximately 6 months after initial deployment. Users were asked about their overall impression, and how well the solution integrates with their workflow as well as how it compares to traditional phone calls to the reading room. Forty of 71 referring providers and 27 of 44 radiologists responded to our survey. VR3 was rated 4.7 out of 5 stars by referrers and 4.1 by radiologists. Seventy percent of referrers and radiologists preferred VR3 to the phone while 4.5% of referrers and 11% of radiologists preferred the phone. Referring providers and radiologists expressed a positive initial perception of the Virtual Radiology Reading Room and prefer it to traditional phone calls to the reading room.
Keywords: Asynchronous; Communication; Consultation; Reading room; Value; Virtual.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Communicating Radiology Test Results: Are Our Phone Calls Excessive, Just Right, or Not Enough?Acad Radiol. 2018 Mar;25(3):365-371. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2017.09.015. Epub 2017 Nov 23. Acad Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29174190
-
Technology-Assisted Virtual Consultation for Medical Imaging.J Am Coll Radiol. 2016 Aug;13(8):995-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2016.02.029. Epub 2016 Apr 12. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016. PMID: 27084068
-
Virtual reading room for diagnostic radiology.Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2024 Mar-Apr;53(2):230-234. doi: 10.1067/j.cpradiol.2023.12.002. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2024. PMID: 38245428
-
Communication - a lost art?Pediatr Radiol. 2022 Apr;52(4):613-615. doi: 10.1007/s00247-021-05133-5. Epub 2021 Jun 26. Pediatr Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34173851 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Radiology Virtual Reading Room: During and Beyond the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Digit Imaging. 2021 Apr;34(2):308-319. doi: 10.1007/s10278-021-00427-4. Epub 2021 Feb 23. J Digit Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33620622 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reading Room Interruptions are Less Disruptive When Using Asynchronous Communication Methods.J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 Oct;37(5):2038-2046. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01073-2. Epub 2024 Mar 19. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024. PMID: 38504083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McGinty GB, Allen B, Geis JR, Wald C. IT Infrastructure in the Era of Imaging 3.0. J Am Coll Radiol 2014;11:1197–204. 10.1016/j.jacr.2014.09.005. - PubMed
-
- IMAGING 3.0 n.d.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

