Genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of bovine mastitis-associated Staphylococcus aureus strains from India
- PMID: 36698060
- PMCID: PMC9878985
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-022-09090-7
Genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of bovine mastitis-associated Staphylococcus aureus strains from India
Abstract
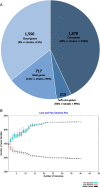
Background: Bovine mastitis accounts for significant economic losses to the dairy industry worldwide. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common causative agent of bovine mastitis. Investigating the prevalence of virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance would provide insight into the molecular epidemiology of mastitis-associated S. aureus strains. The present study is focused on the whole genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of 41 mastitis-associated S. aureus strains isolated from India.
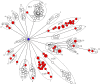
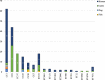
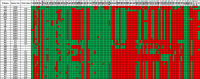
Results: The results elucidate explicit knowledge of 15 diverse sequence types (STs) and five clonal complexes (CCs). The clonal complexes CC8 and CC97 were found to be the predominant genotypes comprising 21 and 10 isolates, respectively. The mean genome size was 2.7 Mbp with a 32.7% average GC content. The pan-genome of the Indian strains of mastitis-associated S. aureus is almost closed. The genome-wide SNP-based phylogenetic analysis differentiated 41 strains into six major clades. Sixteen different spa types were identified, and eight isolates were untypeable. The cgMLST analysis of all S. aureus genome sequences reported from India revealed that S. aureus strain MUF256, isolated from wound fluids of a diabetic patient, was the common ancestor. Further, we observed that all the Indian mastitis-associated S. aureus isolates belonging to the CC97 are mastitis-associated. We identified 17 different antimicrobial resistance (AMR) genes among these isolates, and all the isolates used in this study were susceptible to methicillin. We also identified 108 virulence-associated genes and discuss their associations with different genotypes.
Conclusion: This is the first study presenting a comprehensive whole genome analysis of bovine mastitis-associated S. aureus isolates from India. Comparative genomic analysis revealed the genome diversity, major genotypes, antimicrobial resistome, and virulome of clinical and subclinical mastitis-associated S. aureus strains.
Keywords: Bovine mastitis; MLST; Resistome; Staphylococcus aureus; Virulome; cgMLST.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial resistance and genomic insights into bovine mastitis-associated Staphylococcus aureus in Australia.Vet Microbiol. 2020 Nov;250:108850. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2020.108850. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Vet Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33011663
-
Genome sequencing and comparative genomic analysis of bovine mastitis-associated non-aureus staphylococci and mammaliicocci (NASM) strains from India.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 22;14(1):29019. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80533-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39578587 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular fingerprinting of bovine mastitis-associated Staphylococcus aureus isolates from India.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 27;11(1):15228. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94760-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34315981 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization and clonal diversity of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in milk of cows with mastitis in Brazil.J Dairy Sci. 2013;96(11):6856-6862. doi: 10.3168/jds.2013-6719. Epub 2013 Sep 18. J Dairy Sci. 2013. PMID: 24054305
-
A Global Comparative Genomic Analysis of Major Bacterial Pathogens in Bovine Mastitis and Lameness.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jan 30;15(3):394. doi: 10.3390/ani15030394. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39943164 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive whole genome analysis of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from dairy cows with subclinical mastitis.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 8;15:1376620. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1376620. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38650877 Free PMC article.
-
The metagenomic and whole-genome metagenomic detection of multidrug-resistant bacteria from subclinical mastitis-affected cow's milk in India.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Apr 22;15:1549523. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1549523. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40330015 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and Phenotypic Characterization of Subclinical Mastitis-Causing Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Aug 23;12(9):1353. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12091353. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760650 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the genomic character of the multidrug-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Dhaka, Bangladesh.AIMS Microbiol. 2024 Sep 29;10(4):833-858. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2024036. eCollection 2024. AIMS Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39628721 Free PMC article.
-
Three novel sequencing types from seventeen Staphylococcus aureus genomes isolated from dairy cows milk in the Free State Province of South Africa.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023 Dec 14;12(12):e0073923. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00739-23. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023. PMID: 37966235 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

