Studies on the mechanism of Toxoplasma gondii Chinese 1 genotype Wh6 strain causing mice abnormal cognitive behavior
- PMID: 36698166
- PMCID: PMC9875435
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-022-05618-8
Studies on the mechanism of Toxoplasma gondii Chinese 1 genotype Wh6 strain causing mice abnormal cognitive behavior
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease presents an abnormal cognitive behavior. TgCtwh6 is one of the predominant T. gondii strains prevalent in China. Although T. gondii type II strain infection can cause host cognitive behavioral abnormalities, we do not know whether TgCtwh6 could also cause host cognitive behavioral changes. So, in this study, we will focus on the effect of TgCtwh6 on mouse cognitive behavior and try in vivo and in vitro to explore the underlying mechanism by which TgCtwh6 give rise to mice cognitive behavior changes at the cellular and molecular level.
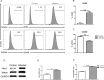
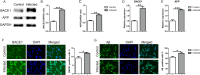
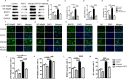
Methods: C57BL/6 mice were infected orally with TgCtwh6 cysts. From day 90 post-infection on, all mice were conducted through the open field test and then Morris water maze test to evaluate cognitive behavior. The morphology and number of cells in hippocampus were examined with hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) and Nissl staining; moreover, Aβ protein in hippocampus was determined with immunohistochemistry and thioflavin S plaque staining. Synaptotagmin 1, apoptosis-related proteins, BACE1 and APP proteins and genes from hippocampus were assessed by western blotting or qRT-PCR. Hippocampal neuronal cell line or mouse microglial cell line was challenged with TgCtwh6 tachyzoites and then separately cultured in a well or co-cultured in a transwell device. The target proteins and genes were analyzed by immunofluorescence staining, western blotting and qRT-PCR. In addition, mouse microglial cell line polarization state and hippocampal neuronal cell line apoptosis were estimated using flow cytometry assay.
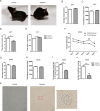
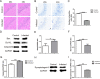
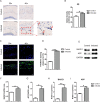
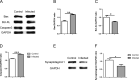
Results: The OFT and MWMT indicated that infected mice had cognitive behavioral impairments. The hippocampal tissue assay showed abnormal neuron morphology and a decreased number in infected mice. Moreover, pro-apoptotic proteins, as well as BACE1, APP and Aβ proteins, increased in the infected mouse hippocampus. The experiments in vitro showed that pro-apoptotic proteins and p-NF-κBp65, NF-κBp65, BACE1, APP and Aβ proteins or genes were significantly increased in the infected HT22. In addition, CD80, pro-inflammatory factors, notch, hes1 proteins and genes were enhanced in the infected BV2. Interestingly, not only the APP and pro-apoptotic proteins in HT22, but also the apoptosis rate of HT22 increased after the infected BV2 were co-cultured with the HT22 in a transwell device.
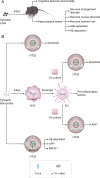
Conclusions: Neuron apoptosis, Aβ deposition and neuroinflammatory response involved with microglia polarization are the molecular and cellular mechanisms by which TgCtwh6 causes mouse cognitive behavioral abnormalities.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Aβ; Cognitive behavior; Hippocampal neuron; Inflammatory response; Toxoplasma gondii Chinese 1 genotype Wh6 strain.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of latent infection of Toxoplasma gondii strains with different genotypes on mouse behavior and brain transcripts.Parasit Vectors. 2025 May 26;18(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s13071-025-06819-7. Parasit Vectors. 2025. PMID: 40420177 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma TgCtwh3 Δrop16 Ⅰ/Ⅲ accelerates neuronal apoptosis and APP production in mouse with acute infection.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025 May 24;18:830-843. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.05.009. eCollection 2025 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40519998 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Chinese I genotype Wh6 strain infection induces tau phosphorylation via activating GSK3β and causes hippocampal neuron apoptosis.Acta Trop. 2020 Oct;210:105560. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2020.105560. Epub 2020 May 31. Acta Trop. 2020. PMID: 32492398
-
Comparative studies of macrophage-biased responses in mice to infection with Toxoplasma gondii ToxoDB #9 strains of different virulence isolated from China.Parasit Vectors. 2013 Oct 26;6(1):308. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-308. Parasit Vectors. 2013. PMID: 24499603 Free PMC article.
-
Trophoblast apoptosis through polarization of macrophages induced by Chinese Toxoplasma gondii isolates with different virulence in pregnant mice.Parasitol Res. 2013 Aug;112(8):3019-27. doi: 10.1007/s00436-013-3475-3. Epub 2013 May 31. Parasitol Res. 2013. PMID: 23722717
Cited by
-
Effects of latent infection of Toxoplasma gondii strains with different genotypes on mouse behavior and brain transcripts.Parasit Vectors. 2025 May 26;18(1):190. doi: 10.1186/s13071-025-06819-7. Parasit Vectors. 2025. PMID: 40420177 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma TgCtwh3 Δrop16 Ⅰ/Ⅲ accelerates neuronal apoptosis and APP production in mouse with acute infection.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025 May 24;18:830-843. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2025.05.009. eCollection 2025 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40519998 Free PMC article.
-
Beyond Latency: Chronic Toxoplasma Infection and Its Unveiled Behavioral and Clinical Manifestations-A 30-Year Research Perspective.Biomedicines. 2025 Jul 15;13(7):1731. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13071731. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40722801 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lentinan has a beneficial effect on cognitive deficits induced by chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection in mice.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Dec 13;16(1):454. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06023-5. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 38093309 Free PMC article.
-
Toxoplasma gondii Reactivation Aggravating Cardiac Function Impairment in Mice.Pathogens. 2023 Aug 9;12(8):1025. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12081025. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37623985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Molan A, Nosaka K, Hunter M, Wang W. Global status of Toxoplasma gondii infection: systematic review and prevalence snapshots. Trop Biomed. 2019;36:898–925. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

