The impact of early empirical antibiotics treatment on clinical outcome of very preterm infants: a nationwide multicentre study in China
- PMID: 36698176
- PMCID: PMC9878784
- DOI: 10.1186/s13052-023-01414-x
The impact of early empirical antibiotics treatment on clinical outcome of very preterm infants: a nationwide multicentre study in China
Abstract
Background: Infants with rule-out infections are responsible for the majority of empirical antibiotics treatment (EAT) in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs), particularly very preterm infants (VPIs). Antibiotic overuse has been linked to adverse outcomes. There is a paucity of data on the association between EAT and clinical outcomes (containing the nutritional outcomes) of VPIs without infection-related morbidities.
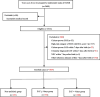
Methods: Clinical data of VPIs admitted in 28 hospitals in 20 provinces of China from September 2019 to December 2020 were collected. EAT of VPIs was calculated as the number of days with initial usage in the first week after birth, and then categorized into 3 groups (antibiotic exposure: none, 1-4 days, and > 4 days). Clinical characteristics, nutritional status , and the short-term clinical outcomes among 3 groups were compared and analyzed.
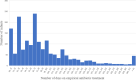
Results: In total, 1834 VPIs without infection-related morbidities in the first postnatal week were enrolled, including 152 cases (8.3%) without antibiotics, 374 cases (20.4%) with EAT ≤4 days and 1308 cases (71.3%) with EAT > 4 days. After adjusting for the confounding variables, longer duration of EAT was associated with decreased weight growth velocity and increased duration of reach of full enteral feeding in EAT > 4 days group (aβ: -4.83, 95% CI: - 6.12 ~ - 3.53; aβ: 2.77, 95% CI: 0.25 ~ 5.87, respectively) than those receiving no antibiotics. In addition, the risk of feeding intolerance (FI) in EAT > 4 days group was 4 times higher than that in non-antibiotic group (aOR: 4.14, 95%CI: 1.49 ~ 13.56) and 1.8 times higher than that in EAT ≤4 days group (aOR: 1.82, 95%CI: 1.08 ~ 3.17). EAT > 4 days was also a risk factor for greater than or equal to stage 2 necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) than those who did not receive antibiotics (aOR: 7.68, 95%CI: 1.14 ~ 54.75) and those who received EAT ≤4 days antibiotics (aOR: 5.42, 95%CI: 1.94 ~ 14.80).
Conclusions: The EAT rate among uninfected VPIs was high in Chinese NICUs. Prolonged antibiotic exposure was associated with decreased weight growth velocity, longer duration of reach of full enteral feeding, increased risk of feeding intolerance and NEC ≥ stage 2. Future stewardship interventions to reduce EAT use should be designed and implemented.
Keywords: Empirical antibiotics treatment; Necrotizing enterocolitis; Very preterm infants; Weight growth velocity.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mortality and extrauterine growth restriction of necrotizing enterocolitis in very preterm infants with heart disease: a multi-center cohort study.Eur J Pediatr. 2024 Aug;183(8):3579-3588. doi: 10.1007/s00431-024-05599-z. Epub 2024 Jun 1. Eur J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38822834
-
The role of nutrition in analysis of risk factors and short-term outcomes for late-onset necrotizing enterocolitis among very preterm infants: a nationwide, multicenter study in China.BMC Pediatr. 2024 Mar 8;24(1):172. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-04611-7. BMC Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38459440 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Practices, Morbidity, and Mortality Among Very Preterm Infants in China.JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Aug 2;4(8):e2118904. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.18904. JAMA Netw Open. 2021. PMID: 34338792 Free PMC article.
-
Early fortification of human milk versus late fortification to promote growth in preterm infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 29;7(7):CD013392. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013392.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32726863 Free PMC article.
-
Early full enteral feeding for preterm or low birth weight infants.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Dec 27;12(12):CD013542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013542.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33368149 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nutritional Strategies for Preterm Neonates and Preterm Neonates Undergoing Surgery: New Insights for Practice and Wrong Beliefs to Uproot.Nutrients. 2024 May 31;16(11):1719. doi: 10.3390/nu16111719. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[A quality improvement project on reducing antibiotic use duration in very low birth weight preterm infants in the neonatal intensive care unit].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jul 15;26(7):736-742. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2311037. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39014951 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Perin J, Mulick A, Yeung D, Villavicencio F, Lopez G, Strong KL, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000-19: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the sustainable development goals. Lancet Child Adolesc Health. 2022;6(2):106–115. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(21)00311-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical