IgE epitopes of Ara h 9, Jug r 3, and Pru p 3 in peanut-allergic individuals from Spain and the US
- PMID: 36698378
- PMCID: PMC9869384
- DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2022.1090114
IgE epitopes of Ara h 9, Jug r 3, and Pru p 3 in peanut-allergic individuals from Spain and the US
Abstract
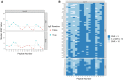
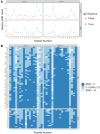
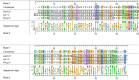
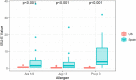
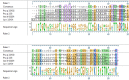
Non-specific lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) are well studied allergens that can lead to severe reactions, but often cause oral allergy syndrome in the Mediterranean area and other European countries. However, studies focused on LTP reactivity in allergic individuals from the United States are lacking because they are not considered major allergens. The goal of this study is to determine if differences in immunoglobulin (Ig) E binding patterns to the peanut allergen Ara h 9 and two homologous LTPs (walnut Jug r 3 and peach Pru p 3) between the US and Spain contribute to differences observed in allergic reactivity. Synthetic overlapping 15-amino acid-long peptides offset by five amino acids from Ara h 9, Jug r 3, and Pru p 3 were synthesized, and the intact proteins were attached to microarray slides. Sera from 55 peanut-allergic individuals from the US were tested for IgE binding to the linear peptides and IgE binding to intact proteins using immunofluorescence. For comparison, sera from 17 peanut-allergic individuals from Spain were also tested. Similar IgE binding profiles for Ara h 9, Jug r 3, and Pru p 3 were identified between the US and Spain, with slight differences. Certain regions of the proteins, specifically helices 1 and 2 and the C-terminal coil, were recognized by the majority of the sera more often than other regions of the proteins. While serum IgE from peanut-allergic individuals in the US binds to peptides of Ara h 9 and its homologs, only IgE from the Spanish subjects bound to the intact LTPs. This study identifies Ara h 9, Jug r 3, and Pru p 3 linear epitopes that were previously unidentified using sera from peanut-allergic individuals from the US and Spain. Certain regions of the LTPs are recognized more often in US subjects, indicating that they represent conserved and possible cross-reactive regions. The location of the epitopes in 3D structure models of the LTPs may predict the location of potential conformational epitopes bound by a majority of the Spanish patient sera. These findings are potentially important for development of peptide or protein-targeting diagnostic and therapeutic tools for food allergy.
Keywords: Ara h 9; Jug r 3; Pru p 3; allergen; allergy diagnosis section manuscript type: original research non-specific lipid transfer proteins; epitope; immunoglobulin E; peanut allergy.
© 2023 Kronfel, Cheng, McBride, Nesbit, Krouse, Burns, Cabanillas, Crespo, Ryan, Simon, Maleki and Hurlburt.
Conflict of interest statement
Author RK and PB were employed by the company Rho Federal Systems Division. Authors RR and RS were employed by the company Aimmune Therapeutics. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
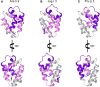
Similar articles
-
Differences in Linear Epitopes of Ara h 9 Recognition in Peanut Allergic and Tolerant, Peach Allergic Patients.Front Allergy. 2022 Jul 22;3:896617. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2022.896617. eCollection 2022. Front Allergy. 2022. PMID: 35935018 Free PMC article.
-
The non-specific lipid transfer protein, Ara h 9, is an important allergen in peanut.Clin Exp Allergy. 2009 Sep;39(9):1427-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2009.03312.x. Epub 2009 Jul 16. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19624524
-
Computationally predicted IgE epitopes of walnut allergens contribute to cross-reactivity with peanuts.Allergy. 2011 Dec;66(12):1522-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02692.x. Epub 2011 Aug 23. Allergy. 2011. PMID: 21883278 Free PMC article.
-
Why lipid transfer protein allergy is not a pollen-food syndrome: novel data and literature review.Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Sep;54(5):198-206. doi: 10.23822/EurAnnACI.1764-1489.206. Epub 2021 May 4. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34092069 Review.
-
Immunotherapy with Pru p 3 for food allergy to peach and non-specific lipid transfer protein: a systematic review.Clin Mol Allergy. 2023 May 31;21(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12948-023-00184-5. Clin Mol Allergy. 2023. PMID: 37259099 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IgE and IgG4 epitopes of the peanut allergens shift following oral immunotherapy.Front Allergy. 2023 Nov 29;4:1279290. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2023.1279290. eCollection 2023. Front Allergy. 2023. PMID: 38093814 Free PMC article.
-
The Diagnosis of Allergy to Lipid Transfer Proteins.Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024 Sep;24(9):509-518. doi: 10.1007/s11882-024-01164-8. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024. PMID: 38990405 Review.
-
Multiplex IgE peanut panels: a critical appraisal of assay designs and the good, the bad, and the ugly features of the applied allergen components.Front Allergy. 2025 Jun 2;6:1515294. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1515294. eCollection 2025. Front Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40529568 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

