Research landscape and trends of melanoma immunotherapy: A bibliometric analysis
- PMID: 36698407
- PMCID: PMC9868470
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1024179
Research landscape and trends of melanoma immunotherapy: A bibliometric analysis
Abstract
Background: Immunotherapy for lung cancer has been a hot research area for years. This bibliometric analysis was intended to present research trends on melanoma immunotherapy.
Method: On April 1, 2022, the authors identified 2,109 papers on melanoma immunotherapy using the Web of Science and extracted their general information and the total number of citations. The authors then conducted a bibliometric analysis to present the research landscape, clarify the research trends, and determine the most cited papers (top-papers) as well as major journals on melanoma immunotherapy. Subsequently, recent research hotspots were identified by analyzing the latest articles in major journals.
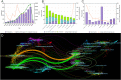
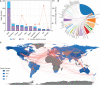
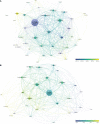
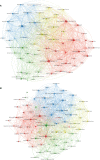
Results: The total and median number of citations of these 2,109 papers on melanoma immunotherapy was 137,686 and 11, respectively. "Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma" by Hodi et al. was the most cited paper (9,824 citations). Among the journals, the top-paper number (16), average citations per paper (2,510.7), and top-papers rate (100%) of New England Journal of Medicine were the highest. Corresponding authors represented the USA took part in most articles (784). Since 2016, the hottest research area has changed from CTLA-4 to PD-1.
Conclusions: This bibliometric analysis comprehensively and quantitatively presents the research trends and hotspots based on 2,109 relevant publications, and further suggests future research directions. The researchers can benefit in selecting journals and in finding potential collaborators. This study can help researchers gain a comprehensive impression of the research landscape, historical development, and current hotspots in melanoma immunotherapy and can provide inspiration for future research.
Keywords: CTLA-4; PD1/PDL1; adoptive cell therapy; bibliometric analysis; clinical trials; immunotherapy; melanoma; tumor mutation burden.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Yu, Liang, Cheng, Jiang, Yu, Zhang, Lu, Qu, Chen and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Keilholz U, Martus P, Punt CJ, Kruit W, Mooser G, Schadendorf D, et al. Prognostic factors for survival and factors associated with long-term remission in patients with advanced melanoma receiving cytokine-based treatments: second analysis of a randomised EORTC melanoma group trial comparing interferon-alpha2a (IFNalpha) and interleukin 2 (IL-2) with or without cisplatin. Eur J Cancer (2002) 38:1501–11. doi: 10.1016/s0959-8049(02)00123-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA, Yang JC, Topalian SL, Schwartzentruber DJ, Weber JS, Parkinson DR, et al. Treatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2. JAMA (1994) 271:907–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

