Bioactive components, pharmacological effects, and drug development of traditional herbal medicine Rubus chingii Hu (Fu-Pen-Zi)
- PMID: 36698464
- PMCID: PMC9868258
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1052504
Bioactive components, pharmacological effects, and drug development of traditional herbal medicine Rubus chingii Hu (Fu-Pen-Zi)
Abstract
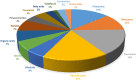
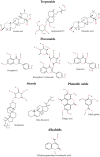
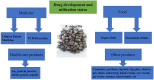
Rubus chingii Hu (Chinese Raspberry), known as Fu-Pen-Zi in Chinese, a woody perennial plant of the genus Rubus in the Rosaceae family, has specific nutritional and medicinal values, which is considered food-medicine herb in China for thousands of years to treat impotence, premature ejaculation, enuresis, frequent urination, and other diseases. This review aims to summarize recent advances in the bioactive components, pharmacological effects, and drug development and utilization of Rubus chingii Hu, hoping to provide useful support for its further research and clinical application. The bioactive components in Rubus chingii Hu contain mainly terpenoids, flavonoids, alkaloids, phenolic acids, polysaccharides, and steroids. The main pharmacological effects are their anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor capacity on human health. Rubus chingii Hu is a very valuable food-medicine herb. The development of Rubus chingii Hu-related drugs is relatively single, which is limited to traditional Chinese medicine and prescriptions. Therefore, it is vital to pay interest to Rubus chingii Hu and its bioactive components in the future and extend its scientific application.
Keywords: Rubus chingii Hu; bioactive components; drug development; pharmacological effects; quality control.
Copyright © 2023 He, Dai, Jin, Liu, Li, Luo, Wang and Kai.
Conflict of interest statement
ZW was employed by Zhejiang Research Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Rubus chingii Hu: A Review of the Phytochemistry and Pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 16;10:799. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00799. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31379574 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The chromosome-scale reference genome of Rubus chingii Hu provides insight into the biosynthetic pathway of hydrolyzable tannins.Plant J. 2021 Sep;107(5):1466-1477. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15394. Epub 2021 Aug 10. Plant J. 2021. PMID: 34174125
-
Rubus chingii Hu: an overview of botany, traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacology.Chin J Nat Med. 2020 Jun;18(6):401-416. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(20)30048-0. Chin J Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 32503732
-
Combined transcriptomic and metabolic analyses reveal potential mechanism for fruit development and quality control of Chinese raspberry (Rubus chingii Hu).Plant Cell Rep. 2021 Oct;40(10):1923-1946. doi: 10.1007/s00299-021-02758-6. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Plant Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34333679
-
Chemical composition, pharmacological activity and development strategies of Rubus chingii: A review.Chin Herb Med. 2024 May 22;16(3):313-326. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2024.01.007. eCollection 2024 Jul. Chin Herb Med. 2024. PMID: 39072206 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Diversity Analysis and Core Germplasm Construction of Rubus chingii Hu.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 23;13(5):618. doi: 10.3390/plants13050618. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38475465 Free PMC article.
-
TCM "medicine and food homology" in the management of post-COVID disorders.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 31;14:1234307. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1234307. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37720220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrated 16s RNA sequencing and network pharmacology to explore the effects of polyphenol-rich raspberry leaf extract on weight control.Front Nutr. 2024 Jan 8;10:1306037. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1306037. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38260083 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-component analyses of raspberry: Optimization of extraction procedure and network pharmacology.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 4;9(11):e21826. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21826. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027894 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of different drying methods on Rubus chingii Hu fruit during processing.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 14;10(2):e24512. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24512. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38312685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Board E. Flora of China. (2010) 2-25.
-
- Que L, Yang G, Li Y, Shan F, Huang LQ. Overview of revision of the catalogue of the substances traditionally considered as both food and chinese medicine. Chin Pharmaceut J. (2017) 52:521–24. 10.11669/cpj.2017.07.001 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

