Improving delineation of the corticospinal tract in the monkey brain scanned with conventional DTI by using a compressed sensing based algorithm
- PMID: 36698482
- PMCID: PMC9873154
- DOI: 10.13104/imri.2022.26.4.265
Improving delineation of the corticospinal tract in the monkey brain scanned with conventional DTI by using a compressed sensing based algorithm
Abstract
Background: The corticospinal tract (CST) is a major tract for motor function. It can be impaired by stroke. Its degeneration is associated with stroke outcome. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) tractography plays an important role in assessing fiber bundle integrity. However, it is limited in detecting crossing fibers in the brain. The crossing fiber angular resolution of intra-voxel structure (CFARI) algorithm shows potential to resolve complex fibers in the brain. The objective of the present study was to improve delineation of CST pathways in monkey brains scanned by conventional DTI.
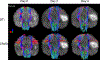
Methods: Healthy rhesus monkeys were scanned by diffusion MRI with 128 diffusion encoding directions to evaluate the CFARI algorithm. Four monkeys with ischemic occlusion were also scanned with DTI (b = 1000 s/mm2, 30 diffusion directions) at 6, 48, and 96 hours post stroke. CST fibers were reconstructed with DTI and CFARI-based tractography and evaluated. A two-way repeated MANOVA was used to determine significances of changes in DTI indices, tract number, and volumes of the CST between hemispheres or post-stroke time points.
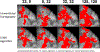
Results: CFARI algorithm revealed substantially more fibers originated from the ventral premotor cortex in healthy and stroke monkey brains than DTI tractography. In addition, CFARI showed better sensitivity in detecting CST abnormality than DTI tractography following stroke.
Conclusion: CFARI significantly improved delineation of the CST in the brain scanned by DTI with 30 gradient directions. It showed better sensitivity in detecting abnormity of the CST following stroke. Preliminary results suggest that CFARI could facilitate prediction of function outcomes after stroke.
Keywords: CFARI; compressed sensing; diffusion tensor imaging; fiber tracking; nonhuman primate; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The authors have conflicts of interests relevant to this study to disclose.
Figures
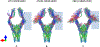

Similar articles
-
Comparing a diffusion tensor and non-tensor approach to white matter fiber tractography in chronic stroke.Neuroimage Clin. 2015 Mar 14;7:771-81. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2015.03.007. eCollection 2015. Neuroimage Clin. 2015. PMID: 25844329 Free PMC article.
-
Resolution of Crossing Fibers with Constrained Compressed Sensing using Traditional Diffusion Tensor MRI.Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2010;7623:76231H. doi: 10.1117/12.844171. Proc SPIE Int Soc Opt Eng. 2010. PMID: 20396591 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking the Corticospinal Tract in Patients With High-Grade Glioma: Clinical Evaluation of Multi-Level Fiber Tracking and Comparison to Conventional Deterministic Approaches.Front Oncol. 2021 Dec 14;11:761169. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.761169. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34970486 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging as a prognostic biomarker for motor recovery and rehabilitation after stroke.Neuroradiology. 2017 Apr;59(4):343-351. doi: 10.1007/s00234-017-1816-0. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Neuroradiology. 2017. PMID: 28293701 Review.
-
Tractography and the connectome in neurosurgical treatment of gliomas: the premise, the progress, and the potential.Neurosurg Focus. 2020 Feb 1;48(2):E6. doi: 10.3171/2019.11.FOCUS19785. Neurosurg Focus. 2020. PMID: 32006950 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- DeVetten G, Coutts SB, Hill MD, Goyal M, Eesa M, O’Brien B, Demchuk AM, Kirton A, Monitor, groups Vs. Acute corticospinal tract Wallerian degeneration is associated with stroke outcome. Stroke. 2010;41:751–6. - PubMed
-
- Mandelli ML, Berger MS, Bucci M, Berman JI, Amirbekian B, Henry RG. Quantifying accuracy and precision of diffusion MR tractography of the corticospinal tract in brain tumors. J Neurosurg. 2014;121:349–58. - PubMed
-
- Yozbatiran N, Keser Z, Hasan K, Stampas A, Korupolu R, Kim S, O’Malley MK, Fregni F, Francisco GE. White matter changes in corticospinal tract associated with improvement in arm and hand functions in incomplete cervical spinal cord injury: pilot case series. Spinal Cord Ser Cases. 2017;3:17028. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
