Negative urgency, PTSD symptoms, and alcohol risk in college students
- PMID: 36698484
- PMCID: PMC9868323
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abrep.2023.100480
Negative urgency, PTSD symptoms, and alcohol risk in college students
Abstract
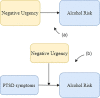
Theoretical models of trauma and alcohol use suggest that trauma-exposed individuals with higher levels of PTSD symptoms are at increased risk of problematic and coping-oriented alcohol use to alleviate unwanted internal states. The goal of the current study was to evaluate whether these associations are enhanced among young adults who report engaging in impulsive behavior in the context of negative affect (i.e., high negative urgency). It was hypothesized that (a) higher negative urgency would be associated with problematic alcohol use; and that (b) negative urgency would moderate the association between PTSD symptoms and problematic alcohol use. Methods: This study used a cross-sectional, secondary data analysis design run on 213 participants: college students, ages 18-25, who endorsed both having an interpersonal traumatic event and current weekly alcohol use. Participants completed a series of assessments and self-report questionnaires. Results: Results of hierarchical linear regression models indicated that greater negative urgency was significantly associated with greater negative alcohol-related consequences and greater coping motives for alcohol, but not past 30-day binge frequency or past 30-day alcohol quantity. Negative urgency did not moderate associations between PTSD symptoms and alcohol outcomes. Conclusions: PTSD symptoms and negative urgency are uniquely associated with indices of alcohol risk in college students with a history of trauma exposure. However, individuals high in negative urgency are not necessarily consuming more alcohol, nor does negative urgency increase the association between PTSD symptoms and drinking outcomes in this population.
Keywords: Alcohol use; Negative urgency; Posttraumatic stress disorder.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms, anxiety sensitivity, and alcohol-use motives in college students with a history of interpersonal trauma.Psychol Addict Behav. 2016 Nov;30(7):755-763. doi: 10.1037/adb0000193. Epub 2016 Oct 27. Psychol Addict Behav. 2016. PMID: 27786512 Free PMC article.
-
Posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms, relationship quality, and risky alcohol use among trauma-exposed students.Addict Behav. 2020 Mar;102:106216. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106216. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Addict Behav. 2020. PMID: 31838368 Free PMC article.
-
Coping, PTSD symptoms, and alcohol involvement in trauma-exposed college students in the first three years of college.Psychol Addict Behav. 2014 Dec;28(4):1052-64. doi: 10.1037/a0038348. Psychol Addict Behav. 2014. PMID: 25528048 Free PMC article.
-
Positive and Negative Pathways Linking Depressive Symptoms to Problematic Alcohol Use Among Argentinian College Students: An Examination of Positive and Negative Urgency Traits and Internal Drinking Motives.J Psychoactive Drugs. 2024 Sep 23:1-10. doi: 10.1080/02791072.2024.2405677. Online ahead of print. J Psychoactive Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39311890
-
Negative affect and alcohol craving in trauma-exposed young adult drinkers.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021 Jul;45(7):1479-1493. doi: 10.1111/acer.14641. Epub 2021 Jul 9. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 34241905 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Noradrenergic Mechanisms and Circuitry of Hyperkatifeia in Alcohol Use Disorder.Biol Psychiatry. 2025 Mar 15;97(6):580-589. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2024.09.009. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Biol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39304172 Review.
-
Sex-related differences in young binge drinkers on the neurophysiological response to stress in virtual reality.Front Public Health. 2024 Jun 14;12:1348960. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1348960. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38947350 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating multilevel, multidomain and multimodal neuroimaging factors to predict early alcohol exposure trajectories using explainable AI.Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025 Jul 15;75:101597. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2025.101597. Online ahead of print. Dev Cogn Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40684513 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams Z.W., Kaiser A.J., Lynam D.R., Charnigo R.J., Milich R. Drinking motives as mediators of the impulsivity-substance use relation: Pathways for negative urgency, lack of premeditation, and sensation seeking. Addictive Behaviors. 2012;37(7):848–855. doi: 10.1016/J.ADDBEH.2012.03.016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Berenz E.C., McNett S., Paltell K. Development of Comorbid PTSD and Substance Use Disorders. Posttraumatic Stress and Substance Use Disorders. 2019;11–27 doi: 10.4324/9781315442648-2. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous