Safety assessment of the process Derchia D.C. Plastics, based on the Starlinger deCON technology, used to recycle post-consumer PET into food contact materials
- PMID: 36698496
- PMCID: PMC9854166
- DOI: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.7759
Safety assessment of the process Derchia D.C. Plastics, based on the Starlinger deCON technology, used to recycle post-consumer PET into food contact materials
Abstract
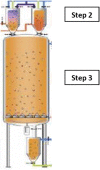
The EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes and Processing Aids (CEP) assessed the safety of the recycling process Derchia D.C. Plastics (EU register number RECYC258), which uses the Starlinger deCON technology. The input material is hot washed and dried poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) flakes originating from collected post-consumer PET containers, e.g. bottles, including no more than 5% PET from non-food consumer applications. The flakes are preheated before being submitted to solid-state polycondensation (SSP) in a continuous reactor at high temperature under vacuum and gas flow. Having examined the challenge test provided, the Panel concluded that the preheating (step 2) and the decontamination in the SSP reactor (step 3) are critical in determining the decontamination efficiency of the process. The operating parameters to control the performance of these critical steps are temperature, pressure and residence time for steps 2 and 3, reduced gas flow rate for step 2 and gas volume/PET mass ratio for step 3. It was demonstrated that this recycling process is able to ensure a level of migration of potential unknown contaminants into food below the conservatively modelled migration of 0.1 μg/kg food. Therefore, the Panel concluded that the recycled PET obtained from this process is not considered to be of safety concern, when used at up to 100% for the manufacture of materials and articles for contact with all types of foodstuffs for long-term storage at room temperature, with or without hotfill. The final articles made of this recycled PET are not intended to be used in microwave or conventional ovens and such uses are not covered by this evaluation.
Keywords: Derchia D.C. plastics Co.; Starlinger deCON; food contact materials; plastic; poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET); recycling process; safety assessment.
© 2023 Wiley‐VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA on behalf of the European Food Safety Authority.
Figures
References
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) , 2008. Guidelines for the submission of an application for safety evaluation by the EFSA of a recycling process to produce recycled plastics intended to be used for manufacture of materials and articles in contact with food, prior to its authorisation. EFSA Journal 2008,6(7):717, 12 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2008.717 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) , 2009. Guidance of the Scientific Committee on transparency in the scientific aspects of risk assessments carried out by EFSA. Part2: General principles. EFSA Journal 2009;7(5):1051, 22 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1051 - DOI
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) , 2021. Administrative guidance for the preparation of applications on recycling processes to produce recycled plastics intended to be used for manufacture of materials and articles in contact with food. EFSA Journal 2021;18(3):EN‐6512, 30 pp. 10.2903/sp.efsa.2021.EN-6512 - DOI
-
- EFSA CEF Panel (EFSA Panel on Food Contact Materials, Enzymes, Flavourings and Processing Aids CEF) , 2011. Scientific opinion on the criteria to be used for safety evaluation of a mechanical recycling process to produce recycled PET intended to be used for manufacture of materials and articles in contact with food. EFSA Journal 2011;9(7):2184, 25 pp. 10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2184 - DOI
-
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration) , 2006. Guidance for Industry: Use of Recycled Plastics in Food Packaging: Chemistry Considerations. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources