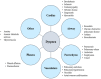
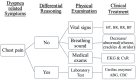
Clinical dyspnea scenario: Using high-fidelity situation simulation teaching program to evaluate learning effectiveness for clinical junior and pre-clinical nurses
- PMID: 36698562
- PMCID: PMC9869138
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1015106
Clinical dyspnea scenario: Using high-fidelity situation simulation teaching program to evaluate learning effectiveness for clinical junior and pre-clinical nurses
Abstract
Background: Confronting a patient's breathing difficulties, clinical junior nurses often do not know how to respond, and fail to give proper evaluation and treatment. Sudden changes in the condition make the clinical nursing novices feel pressured, and even, frustrated.
Objectives: This study aims at exploring the effectiveness of the high-realistic situational simulation of dyspnea teaching program for pre-clinical and clinical 1st year nurses after graduation.
Design: This study adopts a quasi-experimental repeated measure pre-post-test design study with nonequivalent control group pre- and post-test research design. A total of 135 subjects participated in the research: nurses, post graduate year (NPGY) (N = 69), have been employed in the adult ward of a medical center for less than 1 year; and pre-clinical nurses (N = 66), 3rd-year nursing students with nurse licenses from a university in the central part of Taiwan. Simulation-based education instructed and incorporated into the high-realistic situation simulation dyspnea teaching program. Questionnaires were used to measure the effectiveness of learning, data were analyzed with SPSS version 20.0, and the scores were repeatedly measured with the generalized estimating equation.
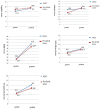
Results: For "cognition, skills, attitude, self-efficacy, teamwork," NPGY and pre-clinical nurses' post-tests are better than pre-tests, with statistically significant results. NPGY nurses' "skills," "attitude" and "teamwork" learning effectiveness are better than those of the pre-clinical nurses.
Conclusion: The high-realistic situational simulation of dyspnea teaching program can significantly improve the learning effectiveness of NPGY nurses and pre-clinical nurses in the clinical evaluation and treatment of dyspnea.
Keywords: dyspnea; high-fidelity situation simulation; learning effectiveness; nurse post graduate year; pre-clinical nurses.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Subeq and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[A prospective before-after self-control study of the scenario simulation teaching of junior nurses in a burns department on the fluid resuscitation care of massive burn patients during shock stage].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021 Aug 20;37(8):781-787. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501120-20201105-00456. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34404165 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Easing student transition to graduate nurse: a SIMulated Professional Learning Environment (SIMPLE) for final year student nurses.Nurse Educ Today. 2014 Mar;34(3):349-55. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2013.04.026. Epub 2013 May 21. Nurse Educ Today. 2014. PMID: 23706963
-
Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
-
[Impact of Nurse Practitioners and Nursing Education on COVID-19 Pandemics: Innovative Strategies of Authentic Technology-Integrated Clinical Simulation].Hu Li Za Zhi. 2021 Oct;68(5):4-6. doi: 10.6224/JN.202110_68(5).01. Hu Li Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34549401 Review. Chinese.
-
Effectiveness of high fidelity simulation versus low fidelity simulation on practical/clinical skill development in pre-registration physiotherapy students: a systematic review.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019 Jun;17(6):1229-1255. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003931. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2019. PMID: 30964770
Cited by
-
Effects of student standardized patients combined with situational simulation on teaching outcomes of acute and severe gastrointestinal tumors.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025 Jul 15;17(7):104773. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i7.104773. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40697220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benner P., Sutphen M., Leonard V., Day L. (2010). Educating Nurses: A Call for Radical Transformation. 1st Edn. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources