The relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being among Chinese junior high school students: A chain mediating model
- PMID: 36698574
- PMCID: PMC9868948
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1053252
The relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being among Chinese junior high school students: A chain mediating model
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to help understand the mechanism behind the relationship between physical exercise and the subjective well-being among Chinese junior high school students, and it is of great significance for the intervention measures to improve the subjective well-being of junior high school students.
Methods: Using stratified cluster sampling method, 1,510 junior high school students (727 males and 783 females) were measured by physical exercise rating scale, perceived social support scale, physical exercise self-efficacy scale, and subjective well-being scale. For data analysis, Pearson's correlation analysis, structural equation model test, and bias-corrected percentile Bootstrap method were carried out in turn.
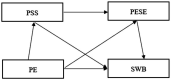
Results: Common method biases can be accepted in this study. (1) There is a positive correlation between physical exercise and subjective well-being, and physical exercise has a significant predictive effect on subjective well-being(β = 0.367 t = 9.415 p < 0.01); (2) Perceived social support partially mediated the relationship between physical exercise and subjective well-being (β = 0.08, t = 3.083, p < 0.01), and its effect ratio is 78.047%; (3) Physical exercise self-efficacy plays a partial mediating role between physical exercise and subjective well-being(β = 0.181, t = 5.132, p < 0.01), accounting for 50.632%; (4) The chain mediating effect of perceived social support and physical exercise self-efficacy was significant (the mediating effect value was 0.028), and the effect amount was 7.629%.
Conclusion: (1) Physical exercise can significantly positively predict the subjective well-being of junior high school students; (2) Physical exercise can also indirectly affect the subjective well-being of junior high school students through the mediating effect of perceived social support and physical exercise self-efficacy. The intermediary effect includes three paths, namely, the individual intermediary effect of perceived social support and physical exercise self-efficacy and the chain intermediary effect of perceived social support physical exercise self-efficacy.
Keywords: junior high school students; perceived social support; physical exercise; physical exercise self-efficacy; subjective well-being.
Copyright © 2023 Yao, Ma, Liu, Cao, Lyu and Guo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The relationship between physical exercise and school adaptation of junior students: A chain mediating model.Front Psychol. 2022 Sep 14;13:977663. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.977663. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36186376 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of physical activity on the subjective well-being of rural left-behind children: the mediating role of discrimination perceptions and loneliness.BMC Psychol. 2024 Aug 26;12(1):455. doi: 10.1186/s40359-024-01950-z. BMC Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39187909 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Physical Exercise and Prosocial Behavior of Junior Middle School Students in Post-Epidemic Period: The Chain Mediating Effect of Emotional Intelligence and Sports Learning Motivation and Gender Differences.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2022 Sep 23;15:2745-2759. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S370495. eCollection 2022. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2022. PMID: 36176377 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Empowering Motivational Climate in Physical Education and Social Responsibility of High School Students: Chain Mediating Effect Test.Front Psychol. 2022 Jan 12;12:752702. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.752702. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35095643 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of physical exercise on social adaptability of college students: Chain intermediary effect of social-emotional competency and self-esteem.Front Psychol. 2023 Mar 22;14:1120925. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1120925. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37034961 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A study on the relationship between high school students' sleep quality, physical exercise, academic stress, and subjective well-being.BMC Psychol. 2025 Mar 1;13(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s40359-025-02497-3. BMC Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40025577 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between physical exercise and sense of social fairness among college students: the chain-mediated role of perceived social support and life satisfaction.Front Psychol. 2024 Aug 20;15:1430492. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1430492. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39228874 Free PMC article.
-
Sports atmosphere and psychological resilience in college students: mediating role of growth mindset.Front Psychol. 2025 Apr 9;16:1532498. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1532498. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40271378 Free PMC article.
-
The mediating effect of resilience and self-efficacy between physical activity and wellbeing: a meta-analytic structural equation modeling.Front Psychol. 2025 Aug 7;16:1621100. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1621100. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40861348 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of physical exercise on adolescent social anxiety: the serial mediating effects of sports self-efficacy and expressive suppression.BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025 Mar 22;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s13102-025-01107-4. BMC Sports Sci Med Rehabil. 2025. PMID: 40121514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bandura A. (1987). Social foundations of thought and action: a social cognitive theory. J. Appl. Psychol. 12:169. doi: 10.2307/258004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

