How relationship-maintenance strategies influence athlete burnout: Mediating roles of coach-athlete relationship and basic psychological needs satisfaction
- PMID: 36698612
- PMCID: PMC9869133
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1104143
How relationship-maintenance strategies influence athlete burnout: Mediating roles of coach-athlete relationship and basic psychological needs satisfaction
Abstract
Introduction: Athlete burnout has many potential negative effects on athletes' sporting performance and careers. Maintaining and promoting the coach-athlete relationship to meet athletes' basic psychological needs is one way to reduce burnout. Existing studies of the correlation between coach-athlete relationships and athlete burnout have mainly focused on the coaches' leadership style, with little attention given to relationship-maintenance strategies and the mechanism of athlete burnout from the athletes' perspective.
Methods: Using an online survey of 256 adolescent athletes, we explore the relationship between relationship-maintenance strategies and athlete burnout, including the potential mediating effects of the coach-athlete relationship and basic psychological needs satisfaction.
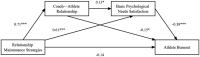
Results: (1) Athletes' relationship-maintenance strategies negatively predicted athlete burnout. (2) Besides the direct effect, we found evidence to support three mediation paths: (a) the coach-athlete relationship, (b) basic psychological needs satisfaction, and (c) both as serial mediators.
Discussion: These findings enhance understanding of the mechanism of athlete burnout, demonstrating the influence of factors beyond the coach's role. The study also provides a theoretical basis for practical intervention by coaches, athletes, and sports organizations to reduce athlete burnout by focusing on athletes' perspectives.
Keywords: athlete burnout; basic psychological needs satisfaction; coach–athlete relationship; mental fatigue; relationship-maintenance strategies.
Copyright © 2023 Fan, Chen, Chen, Li, Guo, Shi, Yang, Yang, Yang, Ding and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How coach leadership behavior influences athletes' performance: the chain-mediated role of the coach-athlete relationship and psychological fatigue.Front Psychol. 2025 Jan 22;15:1500867. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1500867. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 39911198 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of coaches' autonomy support on athletes' aggressive behavior and athlete burnout: verification of the mediating effects of coach-athlete relationship and team efficacy.Front Psychol. 2024 Jul 30;15:1388185. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1388185. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39139597 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of leadership style on coach-athlete relationship, athletes' motivations, and athlete satisfaction.Front Psychol. 2022 Dec 12;13:1012953. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1012953. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36578680 Free PMC article.
-
Mental Health in Elite Coaches.Sports Health. 2024 Nov-Dec;16(6):1050-1057. doi: 10.1177/19417381231223472. Epub 2024 Jan 21. Sports Health. 2024. PMID: 38246889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From adversity to adaptation: the struggle between resilience and athlete burnout in stressful situations.Front Psychol. 2025 May 30;16:1578198. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1578198. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40519831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring potential mediating mechanisms between maladaptive perfectionism and athlete burnout based on multi-theory perspectives.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 13;15:1416281. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1416281. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39346511 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of Factors Predicting Sport Coaches' Perceived Performance.Sports (Basel). 2025 Mar 10;13(3):83. doi: 10.3390/sports13030083. Sports (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137807 Free PMC article.
-
Culture, emotion, and cognition: Understanding the psychological dynamics of Chinese sports with emotional regulation skills and cognitive reappraisal.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 8;10(14):e34306. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34306. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39108858 Free PMC article.
-
Association between coach-athlete relationship and athlete engagement in Chinese team sports: The mediating effect of thriving.PLoS One. 2023 Aug 17;18(8):e0289979. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0289979. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37590239 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between cumulative family risk and athlete burnout among Chinese college athletes: the mediating role of negative affect.Front Psychol. 2023 Oct 16;14:1251663. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1251663. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37908814 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adie J. W., Jowett S. (2010). Meta-perceptions of the coach-athlete relationship, achievement goals, and intrinsic motivation among sport participants. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol. 40, 2750–2773. doi: 10.1111/j.1559-1816.2010.00679.x - DOI
-
- Ai L. X., Wang Y. C. (2017). Proactive personality and coach-athlete relationship: the mediation of self-determined motivation. Chin. J. Clin. Psych. 6, 1119–1123. doi: 10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2017.06.027 - DOI
-
- Ariani D. W. (2019). Basic psychological needs as predictors of burnout and engagement. J. Psychol. Educ. Res. 27, 51–74.
-
- Canary D. J., Stafford L. (Eds.) (1994). “Maintaining relationships through strategic and routine interaction” in Communication and Relational Maintenance (San Diego, CA: Academic Press; ). 3–22.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources