Longitudinal monitoring of pancreatic islet damage in streptozotocin-treated mice with optical coherence microscopy
- PMID: 36698658
- PMCID: PMC9841987
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.470188
Longitudinal monitoring of pancreatic islet damage in streptozotocin-treated mice with optical coherence microscopy
Abstract
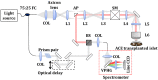
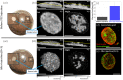
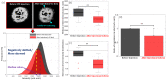
Pancreatic islets regulate glucose homeostasis in the body, and their dysfunction is closely related to diabetes. Islet transplantation into the anterior chamber of the eye (ACE) was recently developed for both in vivo islet study and diabetes treatment. Optical coherence microscopy (OCM) was previously used to monitor ACE transplanted islets in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice for detecting autoimmune attack. In this study, OCM was applied to streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic mouse models for the early detection of islet damage. A custom extended-focus OCM (xfOCM) was used to image islet grafts in the ACE longitudinally during STZ-induced beta cell destruction together with conventional bright-field (BF) imaging and invasive glucose level measurement. xfOCM detected local structural changes and vascular degradation during the islet damage which was confirmed by confocal imaging of extracted islet grafts. xfOCM detection of islet damage was more sensitive than BF imaging and glucose measurement. Longitudinal xfOCM images of islet grafts were quantitatively analyzed. All these results showed that xfOCM could be used as a non-invasive and sensitive monitoring method for the early detection of deficient islet grafts in the ACE with potential applications to human subjects.
© 2022 Optica Publishing Group under the terms of the Optica Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
Per-Olof Berggren is founder and CEO of Biocrine, a biotech company that uses the ACE platform in diabetes research. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vivo imaging of type 1 diabetes immunopathology using eye-transplanted islets in NOD mice.Diabetologia. 2019 Jul;62(7):1237-1250. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4879-0. Epub 2019 May 14. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 31087105 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo imaging of murine endocrine islets of Langerhans with extended-focus optical coherence microscopy.Diabetologia. 2009 Aug;52(8):1599-607. doi: 10.1007/s00125-009-1383-y. Epub 2009 May 30. Diabetologia. 2009. PMID: 19484218
-
Longitudinal three-dimensional visualisation of autoimmune diabetes by functional optical coherence imaging.Diabetologia. 2016 Mar;59(3):550-9. doi: 10.1007/s00125-015-3819-x. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Diabetologia. 2016. PMID: 26613896
-
The impact of oxidative stress on islet transplantation and monitoring the graft survival by non-invasive imaging.Curr Med Chem. 2013;20(9):1127-46. doi: 10.2174/0929867311320090003. Curr Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23317098 Review.
-
Towards high resolution optical imaging of beta cells in vivo.Curr Pharm Des. 2010 May;16(14):1595-608. doi: 10.2174/138161210791164153. Curr Pharm Des. 2010. PMID: 20146662 Review.
Cited by
-
Geometric and topological characterization of the cytoarchitecture of islets of Langerhans.PLoS Comput Biol. 2023 Nov 9;19(11):e1011617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011617. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Comput Biol. 2023. PMID: 37943957 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
