Deep learning-based high-speed, large-field, and high-resolution multiphoton imaging
- PMID: 36698678
- PMCID: PMC9841989
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.476737
Deep learning-based high-speed, large-field, and high-resolution multiphoton imaging
Abstract
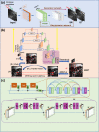
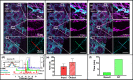
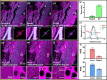
Multiphoton microscopy is a formidable tool for the pathological analysis of tumors. The physical limitations of imaging systems and the low efficiencies inherent in nonlinear processes have prevented the simultaneous achievement of high imaging speed and high resolution. We demonstrate a self-alignment dual-attention-guided residual-in-residual generative adversarial network trained with various multiphoton images. The network enhances image contrast and spatial resolution, suppresses noise, and scanning fringe artifacts, and eliminates the mutual exclusion between field of view, image quality, and imaging speed. The network may be integrated into commercial microscopes for large-scale, high-resolution, and low photobleaching studies of tumor environments.
© 2022 Optica Publishing Group under the terms of the Optica Open Access Publishing Agreement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Deep learning autofluorescence-harmonic microscopy.Light Sci Appl. 2022 Mar 29;11(1):76. doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-00768-x. Light Sci Appl. 2022. PMID: 35351853 Free PMC article.
-
High-throughput, high-resolution deep learning microscopy based on registration-free generative adversarial network.Biomed Opt Express. 2019 Feb 4;10(3):1044-1063. doi: 10.1364/BOE.10.001044. eCollection 2019 Mar 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2019. PMID: 30891329 Free PMC article.
-
Deep-3D microscope: 3D volumetric microscopy of thick scattering samples using a wide-field microscope and machine learning.Biomed Opt Express. 2021 Dec 10;13(1):284-299. doi: 10.1364/BOE.444488. eCollection 2022 Jan 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2021. PMID: 35154871 Free PMC article.
-
Principles of multiphoton microscopy.Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2006;103(2):e33-40. doi: 10.1159/000090614. Epub 2006 Mar 10. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2006. PMID: 16543762 Review.
-
The Role of Generative Adversarial Networks in Radiation Reduction and Artifact Correction in Medical Imaging.J Am Coll Radiol. 2019 Sep;16(9 Pt B):1273-1278. doi: 10.1016/j.jacr.2019.05.040. J Am Coll Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31492405 Review.
Cited by
-
Towards next-generation diagnostic pathology: AI-empowered label-free multiphoton microscopy.Light Sci Appl. 2024 Sep 14;13(1):254. doi: 10.1038/s41377-024-01597-w. Light Sci Appl. 2024. PMID: 39277586 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling precision: a data-driven approach to enhance photoacoustic imaging with sparse data.Biomed Opt Express. 2023 Dec 4;15(1):28-43. doi: 10.1364/BOE.506334. eCollection 2024 Jan 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2023. PMID: 38223183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nehme E., Weiss L. E., Michaeli T., Shechtman Y., “Deep-STORM: super-resolution single-molecule microscopy by deep learning,” Optica 5(4), 458–464 (2018).10.1364/OPTICA.5.000458 - DOI
-
- Hollon T. C., Pandian B., Adapa A. R., Urias E., Save A. V., Khalsa S. S. S., Eichberg D. G., D’Amico R. S., Farooq Z. U., Lewis S., Petridis P. D., Marie T., Shah A. H., Garton H. J. L., Maher C. O., Heth J. A., McKean E. L., Sullivan S. E., Hervey-Jumper S. L., Patil P. G., Thompson B. G., Sagher O., McKhann G. M., II, Komotar R. J., Ivan M. E., Snuderl M., Otten M. L., Johnson T. D., Sisti M. B., Bruce J. N., Muraszko K. M., Trautman J., Freudiger C. W., Canoll P., Lee H., Camelo-Piragua S., Orringer D. A., “Near real-time intraoperative brain tumor diagnosis using stimulated Raman histology and deep neural networks,” Nat. Med. 26(1), 52–58 (2020).10.1038/s41591-019-0715-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
