Constructing a diversified online neurology teaching model under the COVID-19
- PMID: 36698791
- PMCID: PMC9868292
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1071414
Constructing a diversified online neurology teaching model under the COVID-19
Abstract
Purpose: To construct a diversified and comprehensive network teaching model to provide highly qualified medical teaching in neurology under COVID-19 pandemic.
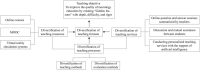
Materials and methods: Published studies on medical education were systematically reviewed and summarized. Based on previous studies and our experience, we constructed a novel online neurology teaching model and applied it to real scene. Students taking traditional in class lessons and online lessons were asked to finish the test, respectively, to compare the efficiency of learning. Questionnaires were designed and assigned to get the feedback from students.
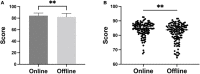
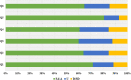
Results: The average test score of students who take online class (84.27 ± 4.64) was significantly higher than those who take in class lessons (82.08 ± 6.17) (P < 0.01). According to the feedbacks from students, online classes were more attractive to students than the conventional one.
Conclusion: Traditional single-mode teaching can no longer meet the needs of current medical education, especially under the rampant epidemic. This novel teaching mode, which orchestrates high-tech tools, diverse teaching methods and traditional teaching concepts, provides the solution to the challenge faced by traditional medical education. We believe that this novel online teaching mode will boost neurology education and inspire educators in other fields during this tough period.
Keywords: COVID-19; education reform; medicine; neurology; online teaching.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Fan, Chen, Zhang, Wu, Hu, Wu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Online education at the medical School of Tongji University during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study.BMC Med Educ. 2021 Sep 28;21(1):512. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02951-x. BMC Med Educ. 2021. PMID: 34583700 Free PMC article.
-
Students' perspective on the online delivery of radiography & medical imaging program during COVID-19 pandemic.J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2021 Dec;52(4S):S68-S77. doi: 10.1016/j.jmir.2021.07.009. Epub 2021 Aug 4. J Med Imaging Radiat Sci. 2021. PMID: 34483086 Free PMC article.
-
Semi-flipped classroom-based learning interventions in a traditional curriculum of oral medicine: students' perceptions and teaching achievements.BMC Med Educ. 2023 Jan 19;23(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12909-023-04017-6. BMC Med Educ. 2023. PMID: 36658530 Free PMC article.
-
Blended and e-learning in pediatric education: harnessing lessons learned from the COVID-19 pandemic.Eur J Pediatr. 2022 Feb;181(2):447-452. doi: 10.1007/s00431-021-04149-1. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Eur J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 34322730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perceptions of medical students towards and effectiveness of online surgical curriculum: a systematic review.BMC Med Educ. 2021 Nov 11;21(1):571. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-03014-x. BMC Med Educ. 2021. PMID: 34763706 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Improving precision instrument cleaning with a quality control module: implementation and outcomes.Front Public Health. 2025 May 14;13:1553113. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1553113. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40438049 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

