Predeposited Autologous Blood Transfusion in Single-Anesthetic Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty with Modern Blood Conservation Strategy
- PMID: 36698982
- PMCID: PMC9851708
- DOI: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.22.00125
Predeposited Autologous Blood Transfusion in Single-Anesthetic Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty with Modern Blood Conservation Strategy
Abstract
This study was performed to examine the hypothesis that the rate of allogeneic blood transfusion in patients who did not predeposit an autologous blood transfusion before single-anesthetic bilateral total knee arthroplasty (TKA) would be noninferior to that in patients who did predeposit blood.
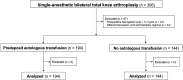
Methods: We assessed the number of allogeneic transfusions required in 338 patients undergoing single-anesthetic bilateral TKA with a preoperative hemoglobin level of ≥11.0 g/dL. All TKAs were performed by a single surgeon according to the same operative and postoperative protocol. All patients received a combination of intravenous and intra-articular tranexamic acid. Neither a pneumonic tourniquet nor a drain was used. The difference in the risk of allogeneic transfusion between patients without and with autologous blood predeposit was compared with a noninferiority margin of 10 percentage points.
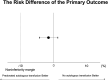
Results: Allogeneic transfusion was required in 1 (0.5%) of 194 patients who predeposited autologous blood and 3 (2.1%) of 144 patients who did not predeposit blood. The difference in risk was -1.6 percentage points (95% confidence interval, -4.1 to 1.0 percentage points); the confidence interval did not include the noninferiority margin and included zero.
Conclusions: In single-anesthetic bilateral TKA, allogeneic transfusion requirements in patients who did not predeposit autologous blood were noninferior to those in patients who predeposited blood.
Level of evidence: Therapeutic Level III. See Instructions for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: The Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest forms are provided with the online version of the article (http://links.lww.com/JBJSOA/A459).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined Intravenous and Intra-Articular Tranexamic Acid in Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty without Tourniquet Use.JB JS Open Access. 2017 Apr 18;2(2):e0002. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.17.00002. eCollection 2017 Jun 26. JB JS Open Access. 2017. PMID: 30229212 Free PMC article.
-
Blood Transfusion can be Avoided in Single-Anesthetic Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2022 Oct;37(10):2020-2024. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2022.05.003. Epub 2022 May 6. J Arthroplasty. 2022. PMID: 35533821
-
Topical intra-articular compared with intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce blood loss in primary total knee replacement: a double-blind, randomized, controlled, noninferiority clinical trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014 Dec 3;96(23):1937-44. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.N.00060. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014. PMID: 25471907 Clinical Trial.
-
Epsilon-aminocaproic acid versus tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis study.J Orthop Traumatol. 2019 Jul 18;20(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s10195-019-0534-2. J Orthop Traumatol. 2019. PMID: 31321578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Perioperative blood management strategies for patients undergoing total knee replacement: Where do we stand now?World J Orthop. 2017 Jun 18;8(6):441-454. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v8.i6.441. eCollection 2017 Jun 18. World J Orthop. 2017. PMID: 28660135 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The necessity of suction drainage when intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid is used during primary total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Jun 18;25(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07604-w. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 38890633 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Minoda Y, Sakawa A, Fukuoka S, Tada K, Takaoka K. Blood management for patients with hemoglobin level lower than 130 g/l in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004 Jun;124(5):317-9. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada S, Kurosaka K, Nishino M, Maeda T, Hirasawa N, Matsue Y. Intraoperative intravenous and intra-articular plus postoperative intravenous tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a placebo-controlled randomized controlled trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020 Apr 15;102(8):687-92. - PubMed
-
- Bong MR, Patel V, Chang E, Issack PS, Hebert R, Di Cesare PE. Risks associated with blood transfusion after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004 Apr;19(3):281-7. - PubMed
-
- Su EP, Su S. Strategies for reducing peri-operative blood loss in total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2016 Jan;98-B(1)(Suppl A):98-100. - PubMed
-
- Cao G, Huang Z, Huang Q, Zhang S, Xu B, Pei F. Incidence and risk factors for blood transfusion in simultaneous bilateral total joint arthroplasty: a multicenter retrospective study. J Arthroplasty. 2018 Jul;33(7):2087-91. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
